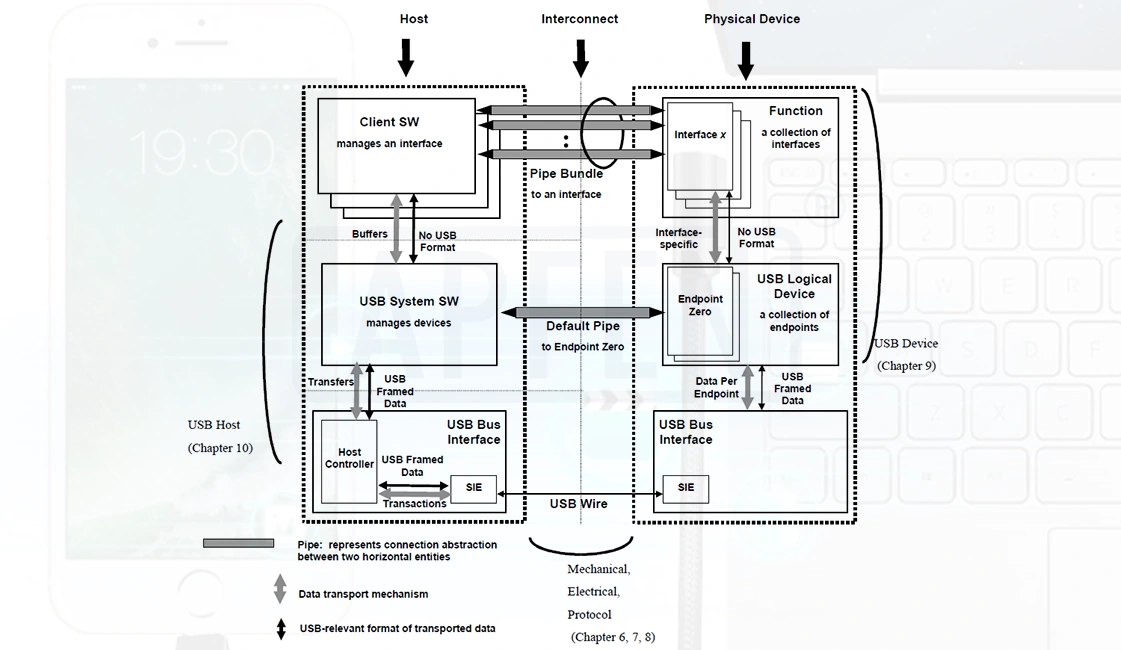
Different Types Of Connector Ports And Their Functions In Modern Devices

Welcome to the exciting world of electronic devices! If you’ve ever looked at the back of your phone, computer, or TV, you’ve probably noticed a bunch of different ports. It can be confusing to understand what they all do and which ones you actually need. But don’t worry, we’re here to help!
In this article, we’ll break down all those connector ports in a way that anyone can understand. We’ll talk about USB, HDMI, Thunderbolt, Ethernet, and more. You’ll learn what each port does and which devices they are commonly used with.
Whether you’re plugging in your phone to charge, connecting your gaming console to your TV, or transferring files between devices, understanding connector ports is essential. No longer are there just one or two types of ports for everything. Now, we have a whole bunch of different connectors for different purposes.
So, join us as we explore the wonderful world of connector ports in our electronic devices. By the time we’re done, you’ll have a clear understanding of what each port does and feel confident in choosing the right ones for your needs. Let’s jump right in!
What types of Apple connector ports are there?
Apple has used several different connectors over the years, starting with the 6-pin FireWire connector on the original iPod in 2001. In 2003, Apple introduced the 30-pin dock connector, which became the standard for connecting Apple devices to computers, chargers, and other peripherals. In 2012, Apple replaced the 30-pin dock connector with the Lightning connector, which is smaller and reversible. More recently, Apple has introduced the USB-C connector with 15 pro max, which offers even more capabilities and versatility. Let’s take a closer look at all the connector types found in Apple devices.
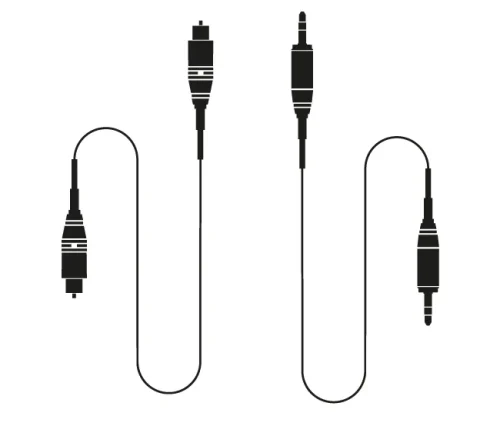
- 6-Pin FireWire Connector:
The 6-pin FireWire connector was the initial connector used in the first-generation iPod. It remained in use until the third-generation iPod, which introduced a new dock connector. While the original iPod had the capability to connect to a dock using FireWire, Apple eventually discontinued all FireWire connectivity in favor of a USB version. - 30-Pin Dock Connector:
The 30-pin Dock Connector was the standard charging and syncing port for Apple devices prior to the introduction of the Lightning connector. It was first introduced in 2003 and was used in various iPods, iPhones, and iPads until 2012. This connector was larger in size compared to the Lightning connector and provided both analog and digital audio output as well as video output. It was eventually replaced by the more compact and versatile Lightning connector. - Apple Lightning Cable:
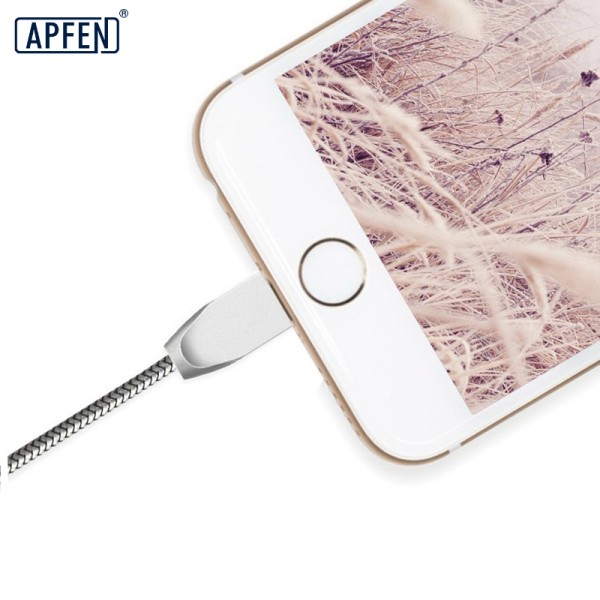
The Lightning cable was introduced in 2012 alongside the iPhone 5 and has since become the standard charging and syncing cable for most Apple devices. It features a reversible design, allowing users to plug it into their devices in either orientation. The Lightning cable supports faster data transfer and charging capabilities compared to its predecessor, the 30-pin Dock Connector. It is a versatile connector used with various Apple devices, including iPhones, iPads, and iPods. - USB-A to Lightning Connector:
The USB-A to Lightning connector is a common variant of the Lightning cable. One end of the cable has a Lightning connector, which plugs into Apple devices, while the other end features a USB-A connector. The USB-A end can be plugged into standard USB ports on computers, wall adapters, or car chargers, providing compatibility with a wide range of devices and charging options. - USB-C to Lightning Connector:
As USB-C technology became more prevalent, Apple introduced the USB-C to Lightning connector. This cable features a Lightning connector on one end and a USB-C connector on the other. The USB-C end can be plugged into modern laptops, tablets, and other devices that support USB-C, offering faster charging and data transfer capabilities. It is especially useful for users with newer MacBook models that feature USB-C ports. - MagSafe Connector:
MagSafe is a magnetic charging connector that was initially introduced with MacBooks and later revived for iPhones. The MagSafe connector attaches magnetically to the back of the iPhone and aligns perfectly for charging. It provides a secure connection but can detach easily to prevent accidental damage. MagSafe supports wireless charging and allows for the attachment of various MagSafe accessories, such as cases and wallets. - USB-C Connector (Latest Transition):
In recent years, Apple has transitioned to using USB-C as the standard port on its MacBooks and iPads. This has led to the introduction of USB-C to Lightning cables, allowing users to connect their iPhones and other Lightning devices directly to USB-C ports. This transition aims to standardize charging across Apple’s product lineup and align with the industry trend toward USB-C as a universal connector for data transfer and charging.
Whatever the connector type make sure to use only orignal iPhone charger. At APPHONE, we understand that your phone is an essential part of your daily life, and that’s why we’re committed to providing you with high-quality digital accessories that you can rely on. Our electronic accessories are designed to be durable, reliable, and easy to use, so you can charge your phone with confidence.
Other than iPhone chargers we offered other product such as USB C cables, Lightning cables, HUB adapters, EarPods, wall chargers, and car chargers.So why settle for a low-quality charger that can slow you down? Upgrade to an original iPhone charger from APPHONE today and experience the difference for yourself!
Different Types of Lightning Connector Chips.
The Lightning connector is more than just a physical connector, it also houses a chip that plays a crucial role in ensuring compatibility and functionality. Apple has developed various Lightning connector chips over the years, each with its own unique features and capabilities. Let’s take a closer look at some of these chips:
First, there’s the C48 chip, which was the original Lightning connector chip used in USB-A to Lightning cables. However, Apple discontinued this chip in 2019, replacing it with newer and more advanced versions. Next, there’s the C52 chip, which is an improved version of the C48 chip. It’s commonly used in quick-charge and high-speed transmission Lightning cables and accessories, and supports fast data synchronization, allowing for shorter charging times and quick file transfers.
The C89 chip is a newer version that replaced the outdated C48 chip in USB to Lightning cables. It offers enhanced security features, ensuring the safe transmission of data between devices. The C94 chip is commonly found in USB-C to Lightning cables, enabling fast charging capabilities. This chip is similar to the C89 chip but is specifically designed for third-party MFi-certified products.
Finally, there are the C100 and C101 chips, which are variations of Lightning connector chips used in specific applications. These chips have their own unique characteristics and are tailored for specific use cases.The Lightning connector chip plays a crucial role in ensuring compatibility and functionality between devices. Apple has developed various chips over the years, each with its own unique features and capabilities. By understanding the different types of chips available, you can choose the right cable or accessory for your needs and ensure a seamless connection between your devices.
What port types are there for USB connectors?
The USB connector series encompasses various physical form factors, each designed to serve specific purposes within a wide range of applications.
- Type A Connector: The Original Standard
The Type A connector is the original and most common USB connector. Recognized for its flat, rectangular shape, it is commonly used to connect downstream peripherals, such as computers and hubs, to a host device. - Type B Connector: Peripheral Device Standard
Often associated with computer peripheral devices like printers and scanners, the Type B connector features a square shape with slightly beveled corners. Like the While the standard Type B connector is still in use, the micro version has gained prevalence in modern applications due to its smaller size. - Type C Connector: The Reversible Interface
The Type C connector is the newest addition to the USB interface family, featuring a reversible symmetrical design that allows insertion with either side up. Highly versatile, it supports USB 3.2, 2.0, and 1.1 signals with data transmission speeds of up to 20 Gbps. - Micro & Mini A&B: Compact Versions for Portability
Micro and Mini A&B connectors are smaller versions of the Type A and B connectors, maintaining high-speed transfer rates of 480 Mbps. These connectors are commonly employed in portable devices, and their On-The-Go (OTG) features allow mobile devices to act as USB hosts. - Type AB Connector: Enhanced Flexibility
The Type AB connector allows both micro A and micro B plugs to connect to a single receptacle type, providing greater flexibility in connection options. This design enables compatibility with different devices utilizing micro A or micro B connectors.
Detailed knowledge about the different USB connectors can be read in our corresponding blog.
What connector types are there for HDMI ports?
In the realm of HDMI connectors, a variety of types cater to different applications. These connectors, while serving the same purpose, are not always interchangeable between devices. The key is to understand the connector type before making a purchase. Currently, five standard HDMI cable connector types exist:
- Type A (Standard):
The Type A HDMI connector stands out as the archetypal and most widely used version, readily recognized by users and found on virtually every modern TV, monitor, game console, and desktop computer. Its prevalence and compatibility make it the standard choice for most consumer electronics. - Type B (Dual-Link):
Type B HDMI connectors, known for their dual-link design, are unique in offering enhanced data transfer capabilities. However, they are not currently used in mainstream consumer products, making them less common in typical applications. The dual-link feature is designed to support higher resolutions and refresh rates, catering to specialized scenarios where such capabilities are essential, such as in certain professional and industrial settings. - Type C (Mini):
The Type C HDMI connector, often referred to as Mini HDMI, is a smaller, more compact version of the standard Type A. Commonly found on portable devices like DSLR cameras, camcorders, and large tablets, these connectors have measurements of 10.42mm x 2.42mm. - Type D (Micro):
Type D HDMI connectors, or Micro HDMI, represent a micro-sized version of standard and mini HDMI connectors. Remarkably smaller with dimensions of 5.83mm x 2.20mm, these connectors were specifically developed for audio-video connectivity in very small, highly portable devices like mobile phones. - Type E (Automotive Connection System):
Type E HDMI connectors, part of the Automotive Connection System, are designed primarily for use in vehicles. While as commonly encountered in typical consumer electronics, these connectors cater to automotive applications where durability, reliability, and specific environmental considerations are crucial. - Male and Female Variants:
HDMI connectors come in both male and female variants. HDMI female connectors are commonly integrated into both signal source devices and receiving devices, serving as sockets for male-end cables. The standard arrangement involves a cable with two male ends plugged into two female sockets simultaneously, facilitating direct wired connectivity between source and display devices.
Male HDMI connectors, typically fixed components at either end of commercially available HDMI cables, are more commonly replaced by swapping in a new cable. However, in situations where cables are routed behind walls or between floors, replacing a damaged male connector might be a more practical and cost-effective solution than replacing an entire cable run. - Straight and Right-Angle HDMI Connectors:
Standard straight HDMI connectors extend horizontally out of the female socket, similar to standard USB cables or 3.5mm jack plugs. This configuration is suitable for most setups. However, right-angled HDMI connectors offer an alternative in scenarios where space in front of the HDMI socket is limited.
Click to read the detailed development history of HDMI technology.
What are the types of MHL connectors?
MHL is the abbreviation of Mobile High-Definition Link. While HDMI remains the default wired audio and video connection protocol for home theaters, MHL (Mobile High-Definition Link) offers an additional way to extend its capabilities. MHL enables the connection of smartphones, tablets, or other portable devices to HDTVs, audio receivers, or video projectors, either through special MHL-enabled HDMI inputs or adapters. Unlike HDMI, MHL not only transmits high-definition video and audio but also charges the connected device simultaneously.
- MHL 1.0:
Introduced in June 2010, MHL 1.0 supports the transfer of up to 1080p high-definition video and 7.1 channel PCM surround audio. It utilizes a mini-HDMI connector on the portable device and a full-size HDMI connector on the MHL-enabled home theater device. The MHL-enabled HDMI port also provides power to the portable device (5 volts/500ma), allowing users to watch movies or listen to music without depleting the device’s battery. - MHL 2.0:
Introduced in April 2012, MHL 2.0 brings improvements such as increased device charging capabilities (4.5 watts at 900ma to 7.5 watts at 1.5 amps) and adds 3D compatibility to the MHL feature set. - MHL 3.0:
Released in August 2013, MHL 3.0 introduces several advancements, including 4K (Ultra HD) signal input, 7.1 channel Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD surround sound support, simultaneous High-Speed Data Channel accessibility, improved Remote Control Protocol (RCP), power and charging up to 10 watts, compatibility with HDCP 2.2, and multiple simultaneous display support (up to 4K monitors or TVs). MHL 3.0 maintains backward compatibility with MHL 1.0 and 2.0 versions. - Super MHL:
Introduced in January 2015, SuperMHL takes a significant leap forward, supporting 8K Ultra HD at 120 Hz, High Dynamic Range (HDR) video, and object-based audio formats like Dolby Atmos and DTS:X. It extends the Remote Control Protocol (RCP) to link and control multiple MHL-compatible devices with a single remote. SuperMHL provides power charging up to 40W, multiple display capability from a single source, and backward compatibility with MHL 1.0, 2.0, and 3.0. - Integrating MHL with USB – MHL Alt Mode:
MHL Consortium’s version 3 protocol integrates with the USB 3.1 framework using a USB Type-C connector, referred to as MHL Alt (Alternate) Mode. This integration allows the USB 3.1 Type-C connector to be compatible with both USB and MHL functions. MHL Alt Mode supports transfer up to 4K Ultra HD video resolution, multi-channel surround audio, simultaneous MHL audio and video, USB data, and power for connected portable devices.
However, it is worth noting: Devices equipped with USB 3.1 Type-C connectors may support MHL Alt Mode, offering users the flexibility to use USB or MHL functions. The USB Type-C connector can accommodate various functions, including HDMI, DVI, or VGA through MHL Alt Mode, allowing for versatile connectivity options.
What are the types of VGA connectors?
VGA (Video Graphics Array) connectors have evolved over the years, and while the core VGA technology has largely been replaced by digital interfaces like HDMI and DisplayPort, various VGA connectors have been developed for specific applications. Here are different types of VGA connectors:
- Standard VGA Connector (DE-15 or HD-15):
The DE-15 or HD-15 VGA connector, featuring 15 pins arranged in three rows, has long served as the standard for analog video output on older computers and monitors. It played a pivotal role in the transition from text-based to graphical displays, providing a widely adopted interface for various applications. - Mini-VGA Connector:
Mini-VGA emerged as a more compact version of the standard VGA connector, catering to smaller laptops and devices where space is limited. While maintaining a similar pin configuration to the standard VGA, the Mini-VGA connector facilitated video output in ultraportable computing devices. - VGA to DVI and VGA to HDMI Adapters:
Adapters like VGA to DVI and VGA to HDMI were introduced to address the need for compatibility between VGA devices and monitors equipped with DVI or HDMI inputs. These adapters not only bridge the gap between different display technologies but often incorporate additional audio connectors, enhancing their versatility. - VGA Over Cat5e/Cat6 Extenders:
VGA over Cat5e/Cat6 extenders revolutionized the transmission of VGA signals over longer distances. Leveraging network cables, these extenders became essential in scenarios such as large conference rooms or auditoriums where the standard VGA reach proved insufficient. - USB to VGA Adapters:
USB to VGA adapters became a solution for connecting VGA displays to computers or laptops lacking native VGA ports. These adapters, often equipped with additional graphics processing capabilities, enabled users to add extra displays to their systems through the more universally available USB ports. - VGA Switch Boxes:
VGA switch boxes addressed the need for managing multiple VGA sources sharing a single display. With multiple VGA inputs and a single VGA output, these devices found applications in conference rooms and control centers, providing a seamless way to switch between various VGA sources.
Despite the evolution of display technologies, these adaptations of VGA connectors and associated technologies highlight their enduring relevance in addressing compatibility issues and facilitating transitions between legacy and modern display standards. If you want to know more about compatibility and application information about VGA cables, then you need to check out our blog here.
Standard Audio AUX Connectors.
Audio AUX connectors, commonly known as auxiliary or simply AUX connectors, are widely used for transmitting analog audio signals. The standard AUX connector is a 3.5mm (1/8-inch) stereo jack, featuring a male plug with three conductive sections (tip, ring, and sleeve). The tip carries the left audio channel, the ring carries the right audio channel, and the sleeve is the common ground.
- TRS (Tip-Ring-Sleeve) Configuration:
The standard 3.5mm AUX connector follows a TRS configuration, where “Tip” represents the left audio channel, “Ring” represents the right audio channel, and “Sleeve” is the ground or common conductor. This configuration allows for stereo audio transmission. - TRS vs. TRRS:
While the traditional AUX connector is TRS, a variant known as TRRS (Tip-Ring-Ring-Sleeve) includes an additional ring. TRRS connectors are commonly found on headphones and mobile devices, supporting stereo audio along with a microphone input. The additional ring enables the microphone to have its dedicated channel, enhancing compatibility with smartphones and other devices that use combined audio and microphone jacks.
AUX connectors find widespread use in audio equipment such as headphones, earphones, speakers, and car stereos. They are also commonly used to connect devices like smartphones, tablets, MP3 players, and laptops to audio playback systems, including speakers, amplifiers, and car audio systems. To learn more details about the most common 3.5mm audio cable among audio AUX cables, you can go to our corresponding blog.
What connector types are available for MyDP ports?
The MyDP connector (Mobility DisplayPort) was introduced in 2012 by the Video Electronics Standards Association “VESA” and is sometimes called “SlimPort”. MyDP is an extension of the DisplayPort connectivity standard. Allows audio and video output from mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets to a larger monitor, TV screen or projector. Although Mobility DisplayPort is the MHL version of DisplayPort, it also supports DVI and VGA connections.
MyDP (Mobile Display Port) typically connects using a USB connector, and the exact type of connector may vary. The most common MyDP connectors are based on the Micro-USB or USB Type-C standards. These connectors are designed to transmit video and audio signals over a single cable.
- Micro-USB MyDP Connector:
The Micro-USB MyDP connector is based on the Micro-USB standard, which is a small and widely used connector in many mobile devices. It supports MyDP technology for video and audio transmission. Found on some older devices that adopted Micro-USB for MyDP connectivity. - USB Type-C MyDP Connector:
The USB Type-C MyDP connector utilizes the USB Type-C standard, which is a more modern and versatile connector known for its reversible design and higher data transfer rates. It supports MyDP technology for both video and audio signals. Commonly found on newer smartphones, tablets, and other mobile devices that adopt USB Type-C for MyDP connectivity.
Click to learn more detailed knowledge about DisplayPort technology versions.
OTG Port Connector Types.
USB On-The-Go (OTG) is a specification that allows USB devices, such as smartphones and tablets, to act as hosts, enabling them to connect to and communicate with other USB peripherals. OTG ports are typically found on mobile devices and some specialized equipment. There is no specific “OTG port connector type” per se, OTG can establish communication connections with various connector types (such as USB A/B/C micro). Belongs to the converter/adapter type function. Below are details about each:
- Micro-USB OTG:
Micro-USB is a widely used connector, and many older smartphones and tablets feature a micro-USB port that supports OTG functionality. The micro-USB OTG port allows the device to act as a host, connecting to USB peripherals like flash drives, keyboards, mice, and more. - USB Type-C OTG:
USB Type-C is a more modern and versatile connector that has become increasingly common in smartphones, tablets, and laptops. USB Type-C ports often support OTG functionality, allowing the connected device to act as a host for various USB peripherals.
USB Type-C OTG ports offer similar functionality to their micro-USB counterparts. Users can connect a wide range of USB peripherals to their USB Type-C OTG-enabled device using an appropriate cable or adapter. To enable OTG functionality, users typically need an OTG cable or adapter. This accessory converts the device’s micro-USB or USB Type-C port into a full-fledged USB host port. The OTG cable or adapter has a standard USB Type-A female connector on one end, allowing users to plug in various USB devices, and a micro-USB or USB Type-C male connector on the other end, which connects to the device’s OTG-enabled port.
Many Android smartphones and tablets support OTG functionality, allowing users to connect USB peripherals. Some laptops and computers with USB Type-C ports also support OTG functionality, although the terminology might differ. For example, on laptops, it may be referred to as “USB Type-C port with OTG support.”
Whether you need customized cables or HUB adapters, APPHONE supports diversified mass customization production services. Includes data cables and charging cables matching different USB types of ports. The professional engineering team supports packaging different types of connectors such as VGA, DVI, AUX, HDMI, Thunderbolt, and various USB connectors into one adapter to achieve multi-function and multi-scenario applications.
What are the various ports and connectors in computer?
Computer ports include audio ports, video ports, networking ports, ports for connecting peripheral devices, USB ports, and more. Modern computers often use USB connections for these purposes, but older systems will have many different kinds of ports.
What are ports in electronics?
A computer port is an interface point between an electronic device, such as a laptop computer, and another peripheral device or computer. This connection point enables various functionalities, such as the transmission of data, power, audio and video.
What are the 6 main ports used in a computer system?
- PS/2: As the name suggests, it was introduced with IBM’s Personal Systems/2 series of computers.
- VGA Port: This port is commonly found in computers, projectors, and high definition TVs.
- Digital Video Interface (DVI);
- Display Port;
- RCA Connector;
- Component Video;
Share This Artcle:

Fast delivery
Fastest delivery within 22 days

Quick proofing
Fastest 3-day proofing cycle

After-sale protection
24-month long warranty

1V1Customer Service
Professional customer service follow-up