Navigating the World of Power Plug Standards
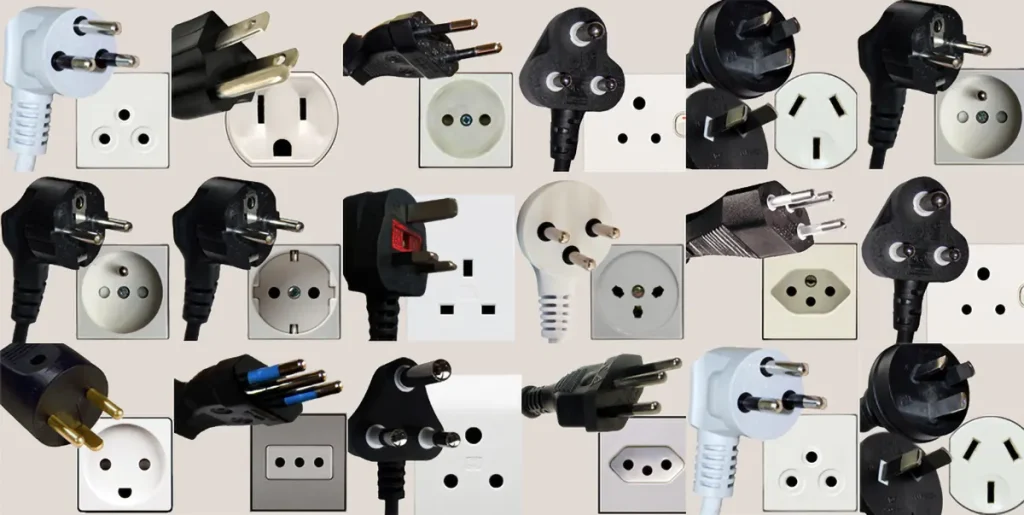

Traveling internationally often means navigating a maze of different power plug standards and electrical systems. As you hop from one country to another, the power outlet shapes and voltage requirements can vary drastically. Failing to account for these differences can lead to frustrating situations where your devices are incompatible or damaged by improper power connections.
In our increasingly connected world, a reliable power source for your electronics is essential, whether you’re a globetrotting digital nomad, a businessperson frequently on the road, or a leisure traveler exploring new destinations. Understanding the complexities of dc power plug standards in the world is crucial to ensuring a seamless and safe charging experience for your laptops, smartphones, cameras, and other gadgets.
Background Introduction
The idea of a unified global plug standard holds an undeniable appeal, particularly for frequent travellers and those managing electrical devices across international borders. Imagine the convenience of being able to seamlessly plug in and use your electronic gadgets without worrying about compatibility issues or carrying multiple adapters. A universal plug standard would not only simplify the user experience but also contribute to reducing electronic waste generated by the production of region-specific plugs and adapters.
However, despite these alluring advantages, establishing a truly global plug standard remains a significant challenge due to the substantial differences in power systems and safety regulations that exist among countries worldwide.
One of the fundamental reasons for the lack of a universal plug standard lies in the varying voltage and frequency standards adopted by different nations. These variances have led to the development and adoption of distinct plug configurations tailored to each country’s specific power requirements.
- Low Voltage: Ranging from 100 to 130 volts, this category is commonly used in countries like the United States, Canada, and parts of Latin America and the Caribbean.
- High Voltage: Ranging from 220 to 240 volts, this category is prevalent in most European countries, China, and several other regions across Asia, Africa, and Australia.
Additionally, the frequency of the alternating current (AC) power supply varies between countries. For instance, countries that prioritize energy efficiency tend to utilize high-voltage and low-frequency systems. Most European nations and China operate at 220-240 volts and a frequency of 50 hertz, while the United States and Canada employ a 110-volt system with a frequency of 60 hertz.
While the primary function of a plug is to connect electrical devices to a power source, plug safety standards across different countries vary significantly, reflecting diverse approaches to electrical safety and regulatory frameworks. These differences can be seen in the design of plugs, the presence or absence of grounding, and the overall emphasis on safety features.
One of the most prominent differences lies in the presence or absence of a grounding prong. Grounding provides a safety mechanism by creating a path for stray electricity to flow to the ground, reducing the risk of electric shock. Many countries, including the United States, Canada, the UK, and most of Europe, have adopted mandatory grounding standards for electrical outlets and plugs. This means that most appliances and devices are designed with three-prong plugs, ensuring a safe connection to the ground. Some countries, like Japan and Australia, have historically relied on double-insulation as a primary safety feature, leading to a prevalence of two-pronged plugs. However, even in these countries, grounding is becoming increasingly common for larger appliances.
Beyond grounding, plug safety standards differ in other aspects. Different countries have adopted distinct plug shapes, often incompatible with each other. This is primarily designed to prevent the use of incorrect plugs and ensure compatibility with local outlets. These variations in plug safety standards have significant implications for both consumers and manufacturers. Travellers often face the challenge of ensuring their devices are compatible with local outlets, requiring the use of adapters or converters.
Differences In Plug Safety Standards In Different Countries
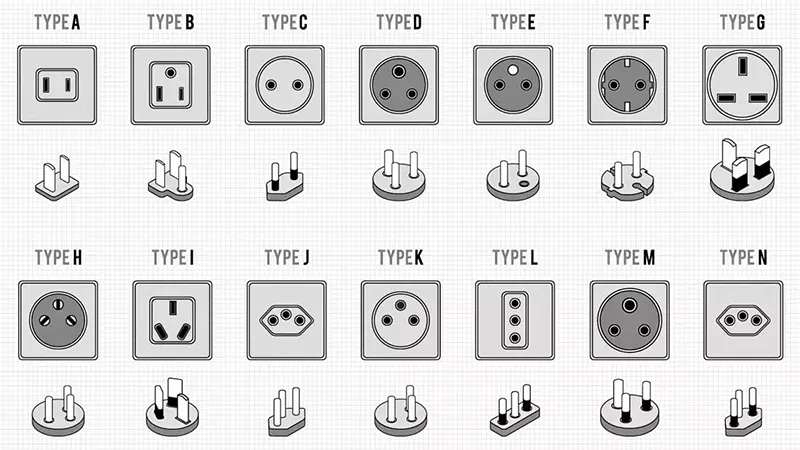
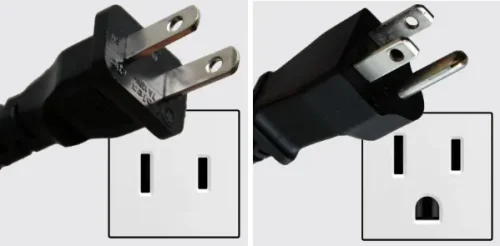
Electrical plug safety standards vary significantly across different regions worldwide, reflecting local infrastructure and safety regulations. In North America, encompassing the USA and Canada, plugs adhere to the National Electrical Code (NEC) and Canadian Electrical Code (CEC). These codes mandate Type A and Type B plugs, featuring grounding pins to prevent electric shocks and ensure proper appliance grounding.
In Europe, the IEC 60906-1 standard is prevalent, with Type C plugs featuring two round pins designed for 230 volts AC at 50 Hz.
The UK utilizes Type G plugs, incorporating specific safety features like fuses and shutters to safeguard against electrical hazards.
In China, GB standards govern electrical plugs, primarily employing Type A, Type C, and Type I plugs. Type A and Type C are used for devices with lower power requirements, while Type I plugs include an earth pin for higher-power appliances.
Middle Eastern countries often adopt Type G and Type D plugs, with variations in voltage requirements and safety specifications tailored to local electrical systems.
These diverse standards ensure compliance with regional safety regulations, mitigating risks associated with electrical installations and appliances across different global contexts. Before travelling to a new country, research the local plug standard to ensure you have the correct adapters and converters for your devices. Using cheap or poorly made USB power adapters can be dangerous and may not provide adequate protection. Always double-check the compatibility of your devices and USB power adapter before plugging them in. Different countries use different voltage levels. Using a device designed for a different voltage can damage it.
Differences In Plug Safety Standards In Different Countries
The world uses a variety of power plug and socket standards, making it crucial to understand compatibility when traveling or using electronics internationally. Common plug types include Type A (US, Canada), Type C (Europe), Type D (India), Type G (UK), and Type I (Australia), among others. Each country also uses specific voltage and frequency standards, with North America typically using 110-120V, 60Hz, and Europe using 220-240V, 50Hz. Most modern electronics are designed for universal voltage compatibility (100-240V), but older devices might require a specific voltage. Plug adapters are used to physically connect devices to different plug types, but they do not convert voltage or frequency. Voltage converters are necessary for devices that are not voltage-compatible. Frequency differences are less common, but some devices might not work properly if the frequency is not compatible. Before travelling, research the plug type and electrical information for your destination, purchase necessary adapters or converters, check device compatibility, and use caution when using electrical appliances in a foreign country. Here is complete detail about all plug types and specifications.
| Detailed Table of Plug Types and Specifications | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plug Type | Rated Voltage | Frequency | Regions Commonly Used | Number of Pins |
| Type A | 100-127 V | 60 Hz | North America, Japan, Taiwan, Mexico | 2 flat parallel pins |
| Type B | 100-127 V | 60 Hz | North America, Central America | 2 flat parallel pins (same as Type A) |
| Type C | 220-240 V | 50 Hz | Europe, South America, Asia, Africa | 2 round pins |
| Type D | 220-240 V | 50 Hz | India, Nepal, Namibia | 3 round pins |
| Type E | 220-240 V | 50 Hz | Europe, Russia, Parts of Asia | 2 round pins, 1 ground pin |
| Type F | 220-240 V | 50 Hz | Europe, Russia, Parts of Asia | 2 round pins, 2 ground pins |
| Type G | 220-240 V | 50 Hz | UK, Ireland, Malta, Malaysia, Singapore, Middle East | 3 rectangular pins |
| Type I | 220-240 V | 50 Hz | Australia, New Zealand, Fiji, Argentina | 2 flat pins in V-shape |
| Type J | 220-240 V | 50 Hz | Switzerland, Liechtenstein | 3 round pins |
| Type K | 220-240 V | 50 Hz | Denmark | 3 rectangular pins, ground pin |
| Type L | 220-240 V | 50 Hz | Italy, Chile | 3 round pins |
| Type M | 220-240 V | 50 Hz | South Africa, India, Pakistan | 3 round pins |
| Type N | 100-127 V / 220-240 V | 50/60 Hz | Brazil | 2 round pins (4mm) & ground / 2 pins (4.8mm) & ground |
| Type O | 220-240 V | 50 Hz | Thailand | 2 round pins, ground pin |
What Are the 5 Common Standard Types Of USB Wall Charger Plugs?
While there are many variations of USB wall charger plugs, here are five common types, categorized by their regional specifications:
US Standard (Type A/B):
The most common type in North America, this plug features two flat parallel prongs (Type A) or two flat parallel prongs with a grounding pin (Type B). These plugs are designed for 120 volts and 60Hz frequency. They are often found on USB wall chargers sold in the US, Canada, and parts of Central and South America.
European Standard (Type C/E/F):
Europe utilizes a family of plug types, all featuring two round prongs. Type C, the most common, lacks grounding. Type E, used in France and similar countries, includes a grounding pin. Type F, prevalent in Germany and other regions, is identical to Type E but with wider slots to accommodate both Type E and Type F plugs. These plugs are designed for 230 volts and 50Hz frequency.
UK Standard (Type G):
This plug features three rectangular prongs, all grounded. It is widely used in the UK, Ireland, and several former British colonies. Type G plugs are designed for 230 volts and 50Hz frequency.
Australian Standard (Type I):
Australian Electrical Plug Standards and New Zealand utilize two versions of Type I. The three-prong version, with three flat pins, is used for larger appliances and is grounded. The two-prong version, lacking a grounding pin, is used for smaller devices. Both are designed for 230 volts and 50Hz frequency.
Chinese Standard (Type C/I):
China uses a combination of Type C (two-pin, round, no grounding) and Type I (three-pin, flat, grounded) plugs. The specific type used depends on the appliance and the region within China. Chinese plugs are designed for 220 volts and 50Hz frequency.
It’s important to note that these are just some of the common USB wall charger plug types. There are many other variations, particularly for specialized applications or specific countries.
Power Plug Wiring Principles and Color Codes
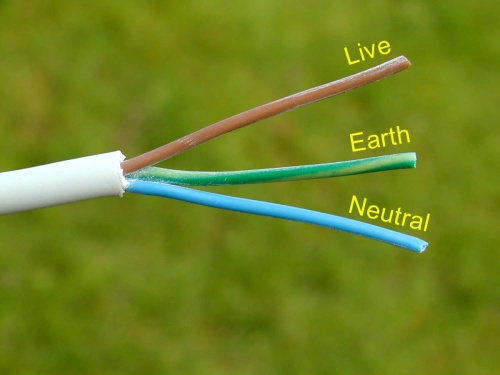
Power plugs are designed to ensure safe and efficient transmission of electricity from the source to the connected appliance. They consist of three main wires: live (L), neutral (N), and ground (E), each serving a distinct purpose and following a specific color code.
- The live wire (L), typically brown, acts as the primary conductor, carrying electricity from the power source to the appliance. It is connected to the terminal marked L in the plug, allowing the flow of current necessary for the device’s operation.
- The neutral wire (N), commonly represented by the color blue, serves as the return path for the electrical current after it has passed through the appliance. This wire connects to the terminal marked N, completing the circuit and enabling the safe return of the current to the source.
- Lastly, the ground wire (E), easily identifiable by its yellow-green color, plays a crucial role in ensuring safety. In the event of an electrical fault or short circuit, this wire provides a dedicated path for the current to flow, effectively preventing electric shocks and minimizing the risk of potential hazards.
In a standard three-core power plug, these wires are designated as E (ground), L (live), and N (neutral), with the brown wire connecting to L, the blue wire to N, and the yellow-green wire to E. Proper polarity and secure connection of these wires are essential for safe operation and minimizing the risk of electrical hazards.
While the color codes for these wires may vary slightly across different regions and standards, the underlying principles remain consistent. For example, in US and Japanese standards, the live wire may be black or brown, while the neutral wire could be white, red, or light blue. However, European standards universally use brown for the live wire and light blue for the neutral wire.
Regardless of the specific color codes, it is crucial to follow the appropriate wiring practices and adhere to the designated standards for your region. Proper installation and maintenance of power plugs and their associated wiring ensure the safe and reliable operation of electrical devices, minimizing the risk of potential hazards and ensuring a seamless user experience.
How to Choose the Right USB Charger Adapter?
Navigating the world of USB charger adapters can be overwhelming, with countless options available. But fear not! This guide will help you choose the right adapter for your needs, ensuring safe and efficient charging for your devices.
- Power Output (Wattage):
This is the most crucial factor, measured in watts (W). Higher wattage means faster charging. Consider the power requirements of your devices. For example, a phone might need 18W, while a laptop might require 65W or even more. If you’re unsure about your device’s power requirements, check its documentation or manufacturer website. - Number of Ports:
This is the most crucial factor, measured in watts (W). Higher wattage means faster charging. Consider the power requirements of your devices. For example, a phone might need 18W, while a laptop might require 65W or even more. If you’re unsure about your device’s power requirements, check its documentation or manufacturer website. - Charging Technology:
Look for adapters that support fast charging technologies like Quick Charge (QC), Power Delivery (PD), or USB Power Delivery (USB-PD). These technologies allow for faster charging speeds and are often indicated by logos on the adapter.
Quick Charge (QC): Developed by Qualcomm, Quick Charge is a popular fast charging standard for Android devices.
Power Delivery (PD): Developed by the USB Implementers Forum, Power Delivery is a more versatile standard that supports a wider range of devices, including laptops, tablets, and smartphones. - Compatibility:
Ensure the adapter is compatible with your devices. Check the voltage and current ratings of both the adapter and your devices to ensure they match. Most modern devices are compatible with a wide range of voltages and currents, but it’s always best to double-check. - Safety Features:
Ensure the adapter is compatible with your devices. Check the voltage and current ratings of both the adapter and your devices to ensure they match. Most modern devices are compatible with a wide range of voltages and currents, but it’s always best to double-check.
Tips for Purchasing a USB Charger Adapter:
- Choose adapters from reputable brands known for their quality and commitment to safety standards. Well-established brands typically use high-quality components and undergo rigorous testing to ensure reliable performance.
- Before making a purchase, take the time to read online reviews from other users. These reviews can provide valuable insights into the adapter’s real-world performance, durability, and any potential issues or limitations.
- Look for adapters that have been certified by recognized organizations like UL (Underwriters Laboratories), CE (Conformité Européenne), or FCC (Federal Communications Commission). These certifications ensure that the adapter meets specific safety standards and has undergone thorough testing.
- While inexpensive adapters may seem tempting, they often lack quality components and crucial safety features. Compromising on quality can potentially put your devices at risk and even pose safety hazards.
- If you anticipate needing to charge multiple devices or devices with higher power requirements in the future, choose an adapter with sufficient wattage and a sufficient number of USB ports. This will prevent the need for frequent adapter replacements and ensure compatibility with your evolving charging needs.
- Before embarking on an international trip, research the plug types and voltage standards of the countries you plan to visit. Purchase a wall charger adapter with the corresponding plug type to ensure compatibility with the local electrical outlets.
- Check the voltage compatibility of your devices and the adapter. Many modern adapters can automatically adjust to different voltage ranges, but it’s always better to confirm compatibility before using them in a new region.
- Consider the size and weight of the adapter, especially if you plan to travel frequently. Compact and lightweight adapters are more convenient to carry and can save valuable space in your luggage.
- Some adapters come with additional features like built-in surge protection, USB ports for data transfer, or compatibility with various charging standards (e.g., USB-C, Quick Charge). Evaluate your specific needs and choose an adapter with features that suit your requirements.
Always prioritize safety and quality when choosing a USB charger adapter. A well-chosen adapter will provide reliable and efficient charging for your devices, ensuring their longevity and your peace of mind.
This concludes today’s article. I hope this information is helpful to you. If you are looking for a reliable USB wall charger brand or power strip, we are here to serve you. At APPHONE, we understand the different needs of businesses and individuals for these electronic accessories. Therefore, we provide comprehensive solutions that go beyond basic charging. With APPHONE, you can customize your charger according to the power plug specifications of different countries, ensuring global compatibility. Need to charge multiple devices at the same time.
What are the electrical standards in the world?
Line voltage standards vary globally between 100 volts and 240 volts, with frequencies of 50 Hz or 60 Hz depending on the country. Referencing a chart specific to the country you plan to visit helps determine the voltage and AC frequency, ensuring compatibility with devices and finding suitable ACUPWR voltage transformers.
What plugs are used around the world?
Different countries utilize various plug types depending on historical adoption and regional standards. Commonly used plugs include Type A and Type B in North America, Type C across Asia and Europe, Type D in India, Type E in parts of Europe, and Type F in Europe and Russia. These variations arose due to historical developments and regional preferences in electrical power plug standards.
Why are plugs different around the world?
The diversity in plug types worldwide stems from historical adoption of electrical systems and innovations at different times. While having a universal standard would be convenient today, the evolution of electrical infrastructure across regions has resulted in the persistence of diverse plug types globally.
Which country has the best electrical standards?
Luxembourg and several other countries in 2019 achieved the highest scores for electricity supply quality. This index considers factors like reliability, voltage consistency, and safety of electrical distribution networks.
What is the IEC standard?
The International Electrotechnical Commission IEC, headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, develops and publishes international standards for electrical, electronic, and related technologies, ensuring interoperability and safety across global markets.
What is the IEC standard for plugs and sockets?
The IEC plug standards 60906-1 and BS 1363 systems share safety features such as polarization and shuttered sockets for line and neutral pins. IEC 60906-1 plugs are rated for up to 16 amperes, while larger BS 1363 plugs are rated for 13 amperes, ensuring safety and compatibility in electrical installations.
Which country plug is best?
The UK plug design features a longer grounding prong compared to the live and neutral prongs, enhancing safety by ensuring the ground connects first when inserting the plug into a socket.
Share This Artcle:

Fast delivery
Fastest delivery within 22 days

Quick proofing
Fastest 3-day proofing cycle

After-sale protection
24-month long warranty

1V1Customer Service
Professional customer service follow-up