Qualcomm QC 4.0 Guide: Version History and Relationship to USB PD.
Qualcomm QC is a public charging technology that allows battery-powered devices (mainly mobile phones) to be charged at power levels exceeding the 5 Volts/2 Amp allowed by standard USB. At the same time, many brand companies also have their own fast charging technology. This article mainly explains the QC fast charging technology without going into details. If you want to know about other brands’ private Quick Charge protocols, Click to read further. Charging has become a necessity in our daily lives, but choosing the right charger and accessories is becoming increasingly important. Let us have a comprehensive understanding of QC protocol.
What is quick charging?
Quick Charge (QC) is a proprietary fast charging technology developed by Qualcomm to increase the charging speed of mobile devices. It does this by managing the power delivered by USB, primarily by communicating with the power source and negotiating voltages. This way, you can charge your device in less time, providing more power. Since the logic is already built into Snapdragon SoCs, mobile electronics manufacturers can add support for the technology with relative ease.
Devices that support fast charging usually include mobile phones equipped with Qualcomm SOC, and require a compatible charger to achieve QC charging. QC technology achieves faster battery charging than standard USB by increasing the voltage, while using technical means to prevent uncontrolled fast charging from causing damage to the battery.
This fast charging technology is widely used in wall chargers, car chargers and some power banks, allowing you to charge your devices faster and reduce waiting time. The use of QC technology not only improves charging efficiency, but also helps extend the life of the device battery.
Features of QC fast charge.
- Fast charging speed:QC allows devices that support this technology to charge at higher current levels, thus filling the battery faster than traditional charging methods.
- Communication between the adapter and the device: Fast charging requires communication between the device and the charging adapter to ensure that the device can safely accept higher currents. The adapter recognizes the connected device and adjusts the output current based on the maximum charging speed it supports.
- Multiple voltage levels: QC supports multiple voltage levels to provide different charging voltages according to the needs of the device. This makes QC suitable for a variety of devices, including smartphones, tablets, Bluetooth headsets, and more.
- Charging efficiency and temperature management:QC charging technology elevates the voltage of a charge while avoiding overheating the USB cable.
- Backwards Compatibility: QC adapters are usually backwards compatible, which means they can be used with devices that don’t support QC, but in this case, the charging speed may be slower.
What are the different versions of QC Quick Charge?
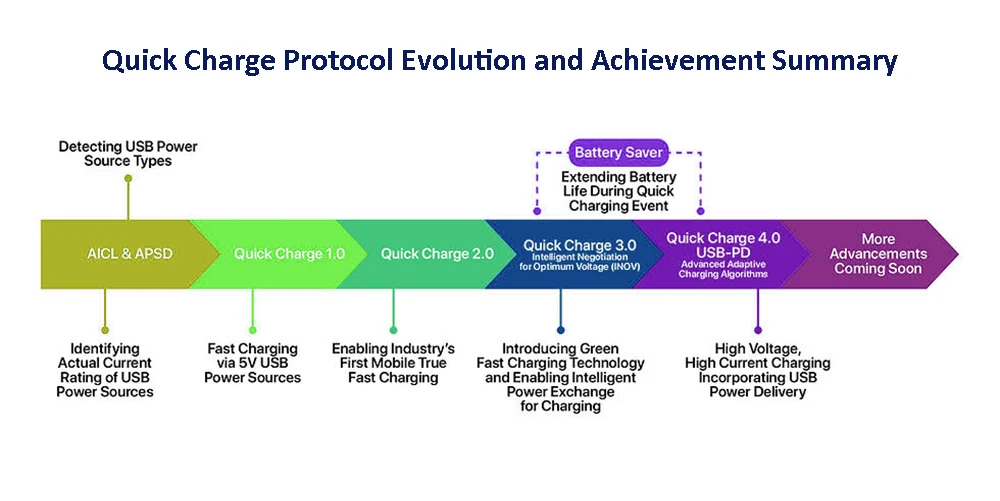
With the advancement of mobile electronic technology, our electronic devices require greater battery capacity and greater performance. Charging efficiency should naturally improve accordingly. Let’s take a look at the evolution of Quick Charge technology:
Quick Charge 1.0
This is the earliest version of QC, launched in 2013. It supports 5V output voltage, a maximum current of 2A, and provides a maximum charging power of 10W.
Quick Charge 2.0
QC 2.0 adds more voltage and current levels, supporting output voltages of 5V, 9V and 12V, with a maximum current of up to 3A. This version also introduces a smarter charging algorithm that dynamically adjusts voltage and current based on the needs of the device and battery. Dual charging technology is also introduced, using two PMICs (power management integrated circuits) to divide power into two shares to reduce the temperature of the phone. This helps optimize charging efficiency and reduce heat generation during charging.
Quick Charge 3.0
Introduces an algorithm called INOV (Intelligent Negotiation of Optimal Voltage), which determines optimal power transfer while maximizing efficiency, providing smarter voltage and current adjustment. In addition, power-saving technology aims to maintain at least 80% of the battery’s original charging capacity, and Qualcomm QC 3.0 has better cooling, 16% faster charging, and 38% higher efficiency than QC 2.0. For QC 3.0 Quick charge with Dual Charge+, the cooling effect is better and the efficiency is increased by 45%.
Quick Charge 4.0
This version was released with the Snapdragon 835 in December 2016. It introduces HVDCP++, optional Dual Charge++, INOV 3.0 and power-saving technology 2. QC 4 supports more voltage levels, including 3.6V, 6V, 9V, 12V and 20V, with a maximum current of up to 4.6A and a maximum power of 100W. Cross-compatibility with USB-C and USB PD specifications. QC 4 also adds additional safety measures, including protection against overvoltage, overcurrent and overheating, as well as cable quality inspection, improving charging safety. Qualcomm claims that the flagship smartphone equipped with the Snapdragon 835 chip can be used for 5 hours longer and only takes 5 minutes to charge, achieving “5 for 5”.
Quick Charge 4+
Released on June 1, 2017, it further improves cooling and charging efficiency for faster, cooler charging. It automatically routes electricity through the coldest path, eliminating potential hot spots and preventing USB-C connectors from overheating, shorting, or damage. Dual Charge++ becomes a mandatory feature. New safety features include monitoring of device case and connector temperature levels, further improving charging safety.
Quick Charge 5
Released on July 27, 2020, it is the fastest QC version so far (2023). Power up to 100W. Qualcomm claims that a phone with a 4500mAh battery can charge 50% in just 5 minutes, Fully charged in 15 minutes. QC 5 is compatible with USB PD PPS programmable power supply and can communicate with the charger. And it introduces hierarchical multi-battery charging technology, which can charge multiple batteries at the same time, greatly improving the charging speed. QC 5 is backwards compatible with all previous QC solutions, ensuring faster charging and higher efficiency.
| Quick Charge versions Development History | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | Release date | Voltage | Current | Power | New function | SOC |
| Quick Charge 1.0 | 2013 | Up to 6.3 V | 2A | 10W | AICL (Automatic Input Current Limit) APSD (Automatic Power Source Detection) | Snapdragon 215, 600 |
| Quick Charge 2.0 | 2014 | Class A: 5 V, 9 V, 12 V; Class B: 5 V, 9 V, 12 V, 20 V; | 1.67 A, 2 A, or 3 A | 18 W (9 V⋅2 A) | HVDCP (High Voltage Dedicated Charging Port); Dual Charge (optional); | Snapdragon 200, 208, 210, 212, 400, 410, 412, 415, 425, 610, 615, 616, 653, 800, 801, 805, 808, 810; |
| Quick Charge 3.0 | 2016 | 3.2 or 3.6 V – 20 V in 0.2 V increments; In 20 mV steps; | 2.6 A, or 4.6 A | 36 W (12 V × 3 A) | HVDCP+; Dual Charge+ (optional); INOV 1.0 & 2.0; Battery Saver Technologies; Integrated cable power capability/identification Various safety mechanisms | Snapdragon 427, 429, 430, 435, 439, 450, 460, 617, 620, 625, 626, 632, 650, 652, 653, 662, 665, 680, 820, 821+765, 765G; |
| Quick Charge 4.0 | 2017 | via QC: 3.6–20 V in 20 mV increments via USB PD: 5 V, 9 V; Via USB PD 3.0 PPS: 3–21 V in 20 mV increments; | 2.6 A or 4.6 A via QC; 3 A via USB PD; | 100 W (20 V⋅5 A) via QC; via USB PD: 27 W; | HVDCP++; Dual Charge++ (optional) INOV 3.0; Battery Saver Technologies 2.0; USB PD compatible; Cable Quality Detection; | Snapdragon 630, 636, 660, 710,720G, 835,845; |
| Quick Charge 4+ | Dual Charge++ (mandatory); Intelligent Thermal Balancing; Advanced Safety Features; | Snapdragon 480, 480+, 4 Gen 1, 670, 675, 678, 690, 695, 6 Gen 1, 712, 730, 730G, 732G, 750G, 765, 765G, 768G, 778G, 780G, 7 Gen 1,855, 855+/860, 865, 865+, 870; | ||||
| Quick Charge 5 | 2020 | / | / | 100W+ | 100W+ charging power; 100% in 15 minutes; Better thermal management (not more than 40°C); Dual Charge; | Snapdragon 865, 865+ |
How to distinguish USB PD from QC?
USB-IF standard USB PD and Qualcomm’s fast charging are the most commonly used public protocols. Their use of different data transfer languages leads to differences in the way they negotiate and handle charging. These are the main differences:
- Technology: USB Power Delivery is the power supply protocol of the USB-IF standards organization. It includes versions 1.0, 2.0, 3.0/3.1, which can support voltages up to 48V and achieve charging power up to 240W. USB PD is proficient in current and voltage negotiation technology, and its main focus is on providing better power transmission.
Quick Charge fast charging protocol is a fast charging protocol from Qualcomm. Its charging voltage may not be as high as the PD protocol, but QC can achieve smarter current, voltage, thermal balance and point-saving technology. The main focus of Qualcomm QC is to provide safer and smarter thermal management fast charging. - Power output: QC and PD chargers have different power output capabilities. The latest version, QC 5.0, is capable of delivering up to 100W of power. The QC charger is designed to work with Qualcomm Snapdragon processors, commonly used in Android smartphones.
The PD charger uses a USB Type-C connector and negotiates the amount of power it can deliver, making it suitable for charging a variety of devices, including laptops and tablets. The latest PD3.1 version can provide up to 240 watts of power, which is more powerful than QC chargers. USB-PD seems to provide higher power output, but in fact, most smartphones currently do not require more than 60W charging power. Of course, some mobile phones that focus on high-performance charging also provide fast charging greater than 100W (mainly concentrated in some mobile phone brands in Asia and China). That’s why Qualcomm’s fast charging is widely adopted by most smartphones, while USB power delivery is better suited for larger devices like laptops and home appliances. - Device Compatibility: The QC charger is designed to work with devices that support Qualcomm Quick Charge technology, while the PD charger is compatible with a wider range of devices, including those that support USB-C Power Delivery.
- Cable compatibility: The PD charger requires a USB-C cable for fast charging, while the QC charger works with USB-C and Micro-USB cables.
- Charging speed: Both QC and PD chargers can provide faster charging speeds, but PD chargers are usually faster than QC chargers. This is because PD chargers can provide more power, allowing faster charging of devices.
- Logo and trademark: USB PD usually uses the “PD” letters and logos, such as “USB PD” or the “PD” icon. QC is usually trademarked with the words “Quick Charge” or “QC”. Checking the logos and trademarks on the charger, device, or charging cable can help you determine which charging standard to use.
It should be noted that some devices may support both USB PD and QC, which means they can choose the appropriate charging standard depending on the charger they are connected to. Therefore, when purchasing chargers and cables, you can check their specifications to ensure that they are compatible with your device and provide the required charging speed.
How do PD and QC4.0 work together?
We learned from the above article that USB Power Delivery (PD) and Quick Charge (QC) are two different charging standards. In QC 3.0 and previous versions, if the USB PD connector is inserted into a QC charging device, the charger can only transmit at the default 5V-1/2A power, which does not fully utilize the potential of USB PD. However, with the release of QC 4.0, QC has the ability to parse PD language. This means QC 4.0 and subsequent versions are compatible with the Power Delivery protocol. When we connect the charger and the device for charging, their workflow is as follows:
First, the USB PD protocol negotiates three key factors: the power required by the device, the maximum transmission power supported by the connected cable, and the maximum power of the charger. These negotiations will determine the maximum power for this charge. Details on the Power Highest specifications for USB Power Delivery can be found on our PD 3.1 blog.
Quick Charge 4.0/5 then steps in and monitors the temperature of the device’s charging process. It implements flexible and intelligent adjustments to ensure that the device does not overheat during charging. This feature is critical to the safety and efficiency of charging.
So the reason QC and PD can work together is that the QC 4.0 charger and subsequent versions has learned to parse the Power Delivery PPS language and upgraded it on top of the QC 3.0 charger, allowing them to work better together. In this way, users can enjoy a more efficient and safer charging experience.
The latest Quick Charge 5 protocol may not be the fastest standard out there. However, it is undoubtedly one of the most established protocols with a long-standing reputation. Additionally, support for USB PD and PPS standards means you don’t have to throw away industry-standard protocols for proprietary protocols like SuperVOOC does.
Device manufacturers make smartphones with specific batteries that can accept a specific amount of power. Battery size and maximum current per cell are design decisions made by the manufacturer and may vary from smartphone to tablet, etc.
Some people may misunderstand that fast charging will damage the battery of the mobile phone. However, the fact is that fast charging operates within the battery design parameters of most smartphones. It just charges the battery the way it was designed to charge.
At APPHONE, we are committed to providing high-quality customized QC charger production services. Whether you need a wall charger or a car charger, we can customize it according to your needs. By choosing APPHONE, you can be sure that your devices will charge under optimal conditions, whether at home, in the office or on the road. Our QC certification guarantees that the charging device you use meets Qualcomm’s performance and safety standards, providing excellent charging performance for your device. If you need efficient, safe and fast charging solutions, please contact us and we will provide you with the best customized service.
QC3.0 vs QC 2.0.
Charging speed: From the above we can understand that QC 2.0 has fixed voltages of 5, 9, and 12V, and the maximum current is 2.7A. This means that its charging is a staged jump.
QC 3.0 offers more voltage levels, including 3.6V, 6.5V, 9V, 12V and 20V, and a higher maximum current, up to 4A. This means QC 3.0 can adapt to the needs of various devices more efficiently, allowing charging to be completed in less time.
Charging efficiency: QC 3.0 introduces the INOV (Intelligent Negotiation of Optimum Voltage) algorithm, which determines the optimal power transfer while maximizing efficiency, thereby improving charging efficiency. Compared with QC 2.0 without INOV, the charging efficiency of QC 3.0 is increased by 38%.
Compatibility: QC 3.0 is backward compatible with QC 2.0, which means QC 3.0-enabled devices and chargers can interoperate with QC 2.0 devices and chargers. This provides users with greater flexibility.
QC3.0 vs QC 4.0.
QC 4.0 is a great improvement over the previous Quick Charge protocol version. The following is a comparison between QC 4.0 and QC 3.0:
- Charging faster, cooler:QC 4.0 charges faster, has a more efficient design, and runs cooler. Compared with QC 3.0, the charging speed of QC 4.0 is increased by 20% and the efficiency is increased by 30%. This means QC 4.0 is able to charge devices faster while generating less heat during the charging process and charging temperatures are 5°C lower, which helps improve charging safety and comfort.
- Intelligent Power Delivery Negotiation: QC 4.0 introduces the USB PD 3.0 PPS language, enabling it to negotiate power output more intelligently. The power output of QC 3.0 is 36W, while QC 4.0 uses a faster charging solution of up to 100W. QC 4.0 also features Dual Charge++ technology that intelligently determines the requested power level based on device needs for optimal power transfer to maximize charging efficiency.
- Safer: QC 4.0 adds multiple layers of protection to prevent battery overcharging. It includes multiple protection measures such as 3 layers of overvoltage protection, 3 layers of overcurrent protection, and 4 layers of overtemperature protection, which improves the safety of charging. In addition, QC 4.0 also has the ability to detect the quality and condition of cables, thereby improving the stability and safety of the charging link.
- Compatibility:In terms of compatibility, please note that QC 3.0 is backward compatible with QC 2.0 and 1.0, but does not support USB PD. QC 4.0 supports USB PD, but is not compatible with QC 2.0 and QC 3.0. If your device supports QC 4.0, then it will be able to utilize the USB PD protocol, but if your device only supports QC 3.0, then it will not be able to achieve QC 4.0 high-speed charging. At the same time, QC 4.0+ has wider compatibility and supports QC 2.0, QC 3.0 and USB PD, providing users with greater flexibility.
To sum up, Quick Charge 4.0 provides faster charging, higher efficiency, smarter power negotiation and enhanced security compared to Quick Charge 3.0. However, to enjoy all the benefits of QC 4.0, you need to make sure you have QC 4.0 capable chargers and devices and understand their compatibility. Contact APPHONE to get a quotation for mass customization of QC4.0 chargers.
Why is QC certification important?
When you buy accessories that are compatible with Quick Charge, it is crucial to look for the Quick Charge logo. This certification ensures the charger meets Qualcomm’s high performance and safety standards. Using a charger that is not certified for fast charging may increase the risk of short circuiting or overheating, causing damage to your device and charger.
The charger may get hot while powering your device, but if it’s certified to be fast charging compatible, you don’t have to worry too much. These certifications represent a series of security measures that have been taken. The controller chip precisely regulates the battery charging current to ensure there aren’t any dangerous spikes in the current, while temperature and voltage controls keep the charger operating stably within safe parameters.
APPHONE has obtained QC certification for its high-quality production technology, which means we can provide you with customized QC charger production services that comply with fast charging standards to meet your specific needs. This way, you can use our products with confidence, ensuring your devices are both efficient and safe when charging.
Share This Artcle:

Fast delivery
Fastest delivery within 22 days

Quick proofing
Fastest 3-day proofing cycle

After-sale protection
24-month long warranty

1V1Customer Service
Professional customer service follow-up











