Complete USB Cable Manufacturing Process Guide

Every day, we use USB cables in daily life, but have you ever wondered how these ordinary-looking cords are made? How are those tiny wires inside your USB cables put together? The process of making USB cords might seem magic, but there’s actual science behind it.
Well, making USB cables is like putting together a puzzle. It involves using cool machines and carefully picking the right parts. All this work helps us connect our devices and charge our phones or transfer files in a snap.
In this journey, we’ll show you what goes on behind the scenes when making USB cables at APPHONE. At APPHONE, we are not just a manufacturer of mass production of USB data cable– we are your trusted partner in your business. In this blog, we’ll talk about everything in the manufacturing process of USB cables, from choosing the right materials to checking each cable to ensure it works perfectly. You’ll got to know how these cables are made and how they keep getting faster and better at transferring data.
How is a USB Cable Constructed?
Manufacturing process of USB cables involves several detailed steps that demand precision and care to guarantee top-notch quality, functionality, and safety. In this thorough guide, we’ll examine each stage of the manufacturing process for cables in detail. Let’s begin.
Step 1: Connector Production
To kick off the manufacturing process, we begin by creating connectors. These connectors are assembled using a semi-automated machine. First, we inject shells into the machine. Then, there are two special cases for this step:
- When making MFI (Made for iPhone/iPad/iPod) cables, the MFI chip will be packaged onto the circuit board at this stage.
- When making a fast-charging cable supporting 100W or more, the E-Marker chip for intelligent power control will be packaged.
After that, the circuit boards are inserted into the shells. Once that’s done, we attach plastic backing pieces to the connectors. This completes the connectors and prepares them for the next stage of mass production of USB data cables.
Step 2: Cable Production
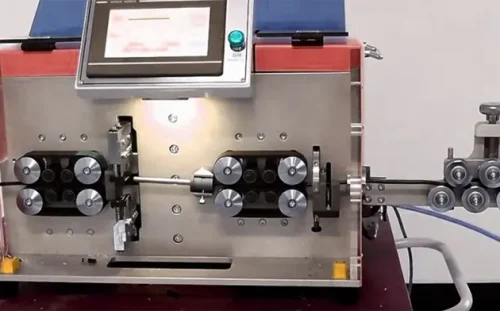
On the next stage of USB data cable production process, we move on to manufacturing the cable, which involves several stages. It all begins with obtaining metal wires, usually copper or aluminum. These wires are created by pulling a copper or aluminum rod through a series of special diamond dies on a machine called a drawbench. This process, called drawing, applies a lot of pressure to the metal rod, making it thinner. After that, the wire is softened and made flexible through a process called annealing.
Once we have the flexible wires, we move on to twisting and stranding them together using a special method to ensure they’re twisted to just the right length. This twisting and stranding process makes the wires more flexible and improves their electrical performance.
After the wires are soft, flexible, and twisted, they’re passed through a machine called an extruder. This machine coats the wires with insulating material, usually plastic, to create a cable. The cable is then cooled down and wound onto reels for further processing.
Step 3: Cable Assembly
The next step in USB cable manufacturing is cable assembly. It involves wrapping wires to create the cable itself based on the desired USB transfer standard and fast charging power requirements.
The first step in cable assembly is winding. The USB transmission standard and the charging power supported by the cable in the future determine the wire core specifications used for winding in this step. The number of pins required to solder a USB connector determines how many wire cores are required. For specific USB wiring schematic diagram knowledge, you can go to our corresponding blog to learn more.
During the winding process, it will be wrapped with shielding net and aluminum foil simultaneously to prevent it from being affected by the current magnetic field during high-speed data transmission. Ensures pure transmission and acts as thermal insulation.
The final step in cable shaping is to wrap the cable in an outer protective layer. It is generally covered with an insulating protective layer such as PVC, TPE or nylon braid. The type of insulation used depends on the intended use of the cable. Once the outer layer is wrapped, the cable is complete and ready for the next production process.
Step 4: Cutting Cable Length
Now, we move on to cutting the cables. These cables start off as raw materials and are pretty long. To turn them into USB cables, we need to cut them into the right lengths, like 1 meter or 2 meters. This way, they’ll be the perfect size to meet what our customers need.
Step 5: Thermal Stripping of the Jacket Material At Both Ends Of The Cable
Once the cables are cut to the right length, the next important step is wire stripping. This means removing the outer insulation of the cable to reveal the inner wires. It’s a crucial step because it gets the wires ready for soldering.
We use special wire stripping machines for this job to make sure it’s done perfectly. The machines carefully remove the outer insulation, making sure not to damage the inner wires. This is important to keep the wires intact and ensure that the cable can still conduct electricity properly. Once the jacket is stripped, we trim the foil and use a machine to twist the inner wires together. This step ensures that the wires are all set and ready for the next part of the process.
Step 6: Solder the Connector to the Cable
In this step, connectors are attached to the internal wire assembly. We start by uncovering the end of each wire. Different connector types, like USB-A, Micro USB, Lightning, and USB-C, have specific pin arrangements. We carefully position the wire cores near these pins to match.
We then use specialized welding machines to handle the welding. Under the supervision of our trained technicians, each exposed wire core is manually fed into the set position of the welding machine. The wire core and connector are transferred to the programmed position by automatic welding equipment and then welded and fixed.
This specialized semi-automatic soldering machine provides controlled heat to melt high-quality solder into each joint sequentially. While working, the machine ensures structural integrity and electrical continuity down to microns.
Once soldering is complete, close visual inspections are conducted using high-powered magnifiers. Technicians examine every connection point to validate full-strength bonds and flawless joins were achieved after soldering process. Only cable assemblies that pass this quality audit move forward to the next stages. Our careful work during the connector attachment ensures smooth transmission between the cable and device, without any signal loss or faults.
Step 7: First Port Shape Injection Molding
In this step, we use an injection molding machine to apply the primary mold to the connector. This mold is crucial for safeguarding the soldered connections. The primary molding, also known as internal molding, acts as the initial layer of protection, enhancing the cable’s stability, strength, and durability. The soldered connectors are pressed with a tough material, usually plastic SGP, to shield them effectively.
Step 8: First Electrical Test
After completing the primary molding, the USB cables proceed to the testing unit for a thorough electrical performance check. This test ensures that the cables have 100% electrical conduction capability. An electrical test device is utilized to assess the electrical efficiency of semi-finished products.
Step 9: Second External Injection Molding/Installation of Port Housing
After completing performance testing, the semi-finished products move on to the external injection molding machine for the final layer of protection. This process typically involves molding the port housing onto the cables. During this step, the soldered connections are firmly pressed with PVC soft material (Poly Vinyl Chloride) to provide an additional layer of protection. Once the over mold has cooled and hardened, the finished products are ready for final testing.
However, it’s worth noting that in some cases, customized cable port shells may not be injection molded. Instead, they may be covered with an independent shell with a more personalized shape. These shells can be made of various materials such as hard plastic or aluminum alloy, depending on the customer’s product design requirements.
Step 10: Second Electrical Performance Test
In the final electrical test, we ensure that the cables maintain effective electrical performance even after undergoing the process of being firmly pressed with heated PVC material. This test verifies that the cables are still functioning properly despite the additional layers of protection they have received.
Step 11: Visual Inspection and Quality Testing
Once the manufacturing process is complete, a critical step is to thoroughly inspect the cables to ensure they meet strict quality standards. Each cable will undergo a rigorous visual inspection before subsequent packaging. During the visual inspection, we carefully inspect each cable for any signs of defects, such as holes or bulges caused by improperly formed ports. This step ensures that each cable meets our high quality appearance standards before delivery. In addition to basic visual inspections, random spot testing is performed.
At this stage, we conduct various aspects of the USB data cable production process quality and performance:
- Push and Pull Force Test: This test evaluates the strength of the cable by measuring the force required to push or pull it. It ensures that the cable can withstand typical usage scenarios without breaking or becoming damaged.
- Salt Spray Test: The salt spray test assesses the cable’s resistance to corrosion and rust. Samples are exposed to a saline mist to simulate harsh environmental conditions, such as exposure to saltwater or humidity.
- Swing Tensile Test: This test evaluates the cable’s tensile strength and flexibility. It involves subjecting the cable to repeated bending and stretching to ensure it can withstand frequent movements without weakening or breaking.
- Pull and Plug Test: This test assesses the durability of the cable’s connectors by repeatedly inserting and removing them. It ensures that the connectors maintain a secure connection over time, even with frequent use.
- Constant Temperature Test:The constant temperature test evaluates the cable’s performance under extreme temperature conditions. Samples are exposed to high and low temperatures to assess their resilience and functionality in different environments.
By conducting these rigorous quality tests, we identify any potential defects or issues and ensure that only high-quality cables are delivered to customers. This meticulous quality control process helps us uphold the reputation of the brand and ensures customer satisfaction with the product.
Step 12: Cooperate with OED&ODM to Customize Brand Packaging
The next step in the cable manufacturing process is customized branded packaging. At APPHONE, we specialize in OEM&ODM services, which are integral to our manufacturing process. In addition to our core services, we offer a range of customized solutions to meet our customers’ branding and promotional needs. These include laser engraving, screen printing, and the design of both internal and external packaging materials and styles.
From designing the packaging layout to procuring the materials, we work to deliver packaging solutions that align with our brand identity and meet the expectations of our customers.
Step 13: Packaging Process
In this step, we focus on packaging the cables effectively to ensure they reach our customers in perfect condition. Our packaging process includes several key components:
- Twisted Wire Method: The cables are carefully arranged using the twisted wire method to prevent tangling and ensure they remain neat and organized during transportation and storage.
- Bundling: We bundle the cables together securely to prevent any damage or fraying during transit. This ensures that the cables stay protected and maintain their quality until they reach the end user.
- Inner Packaging: Once bundled, the cables are placed in inner packaging materials such as boxes or bags. These inner packaging materials provide additional protection and cushioning to safeguard the cables from bumps and impacts during shipping.
- Outer Packaging: Finally, the inner packaging containing the cables is placed into outer packaging materials such as corrugated cardboard boxes or envelopes. The outer packaging provides an additional layer of protection and serves as the primary barrier against external elements, ensuring the safe delivery of the cables to our customers.
Step 14: Delivery Process
In addition to arranging logistics delivery, we offer flexibility by providing options for delivery to our customer’s preferred freight forwarder. Our delivery process includes the following steps:
- We coordinate with trusted logistics partners to ensure efficient and timely delivery of the cables to our customers’ specified locations. Our logistics team handles all aspects of the delivery process, from scheduling pickup to tracking the shipment’s progress until it reaches its destination.
- We also accommodate our customers’ preferences by offering the option to deliver the cables directly to their chosen freight forwarder. This allows customers to have greater control over the shipping process and seamlessly integrate the delivery into their existing supply chain operations.
Collaborate with APPHONE: Your Ultimate USB Cable Partner
The above is the normal process for starting mass production. In the case of special customized products, we will provide free proofing services before mass production of USB data cable to ensure that the product functions meet customer expectations. We understand that every customer has unique requirements, and we are committed to providing tailored solutions to meet their needs. For special customized products, we offer free proofing services to ensure that the final product meets our customer’s specifications and expectations. This additional step underscores our commitment to delivering exceptional quality and ensuring customer satisfaction.
At APPHONE, we are dedicated to providing superior products and services that exceed our customers’ expectations. Our comprehensive the manufacturing process for cables and commitment to customer satisfaction make us the preferred choice for all your cable needs. Collaborate with APPHONE for best experience.
At APPHONE, we take pride in our commitment to excellence and customer satisfaction. Our meticulous attention to detail, innovative manufacturing processes, and dedication to quality ensure that we deliver premium products that meet the highest standards. We support the production of many different styles of USB data cables, adapters, Fast chargers, audio headsets and car chargers. Focus on innovation and pursue quality. We strive to exceed our customers’ expectations at every step of the way, from design to delivery.
How is a USB cable constructed?
Raw cables are made up of different wires which are braided and foiled to prevent electromagnetic interference. In this step, the outer jacket is stripped using a stripping machine to reveal the inner conductors so they can be linked to the connector properly.
What is the manufacturing process of a cable?
The manufacturing process of a Medium Voltage cable is divided into seven stages: incoming feed, polymer feed, triple extrusion, thickness control, cross-linking, cooling and collection.
What is inside a USB cable?
The most basic USB cable U structure contains four wires, two for power and two for data. The data wires are 28 AWG, the power wires are 20 to 28 AWG. The power cores are un-twisted and the data lines twisted.
What material is used for USB cable insulation?
Insulation for twisted pair should be PE, while insulation for others is not required, usually PVC. The specific gauge and insulation for twisted pair are to guarantee characteristic impedance.
What is the best material for USB cables?
Now, tell you idea how to choose good usb cable . First , look material, in the market , there more have PVC, TPE, nylon braided cable. PVC is cheapest material, It touch very hard,it’s not easy collect it. TPE material is very soft, environment friendly, flexible, easy to collect.
What are the raw materials for cable manufacturing?
Rubber, copper, aluminum, thermoplastic, thermosets, and other plastics are used in wire and cable.
The common materials used in the construction of cables core include copper and aluminium for conductors, due to their excellent electrical conductivity. Insulation is typically provided by materials like PVC, rubber, or high-density polyethylene.
How to make a long USB cable?
If you want to extend the USB signal more than 25 meters, you need to use a USB extender. USB extenders usually consist of a transmitter(TX) and a receiver(RX). To extend the distance between your peripheral devices and the USB port, connect the TX and RX via a CATx cable. For general USB cable length restrictions and comprehensive cable extension methods, you can go to the corresponding blog to learn more.
Share This Artcle:

Fast delivery
Fastest delivery within 22 days

Quick proofing
Fastest 3-day proofing cycle

After-sale protection
24-month long warranty

1V1Customer Service
Professional customer service follow-up