In the digital age, we are always accompanied by various charging and connecting devices. Have you ever wondered what kind of “secret” is hidden in the internal structure of those seemingly ordinary USB cables? Imagine the incredible speed at which data and power are being transferred inside these tiny cables the moment you connect your device. They are like the couriers of the digital world, silently delivering information to your device. But the story behind these data line structures is much more than that. Their outsourcing materials, port types, and even internal structures all affect your experience and device performance.
So, wonder why some cables are flexible and durable, while others are prone to tangles and damage? Or do you want to know the differences and commonalities between USB-C, Lightning and other port types? Or, do you want to learn more about the structure of the inner core of the USB cable transmission line, and the hidden technology behind those complicated wiring diagrams? Whether you are a novice or a technology enthusiast, this article will take you to explore the mysteries of USB cable structure in an easy-to-understand way, so that you can better understand and trust these seemingly ordinary “wires” in daily use. magic. Are you ready? Today, APPHONE will unveil the mystery of these cables, from cable outsourcing materials, port types, to cable transmission line inner core structure and USB cable wiring diagram, decode them for you one by one, and take you into the wonderful world of USB cables.
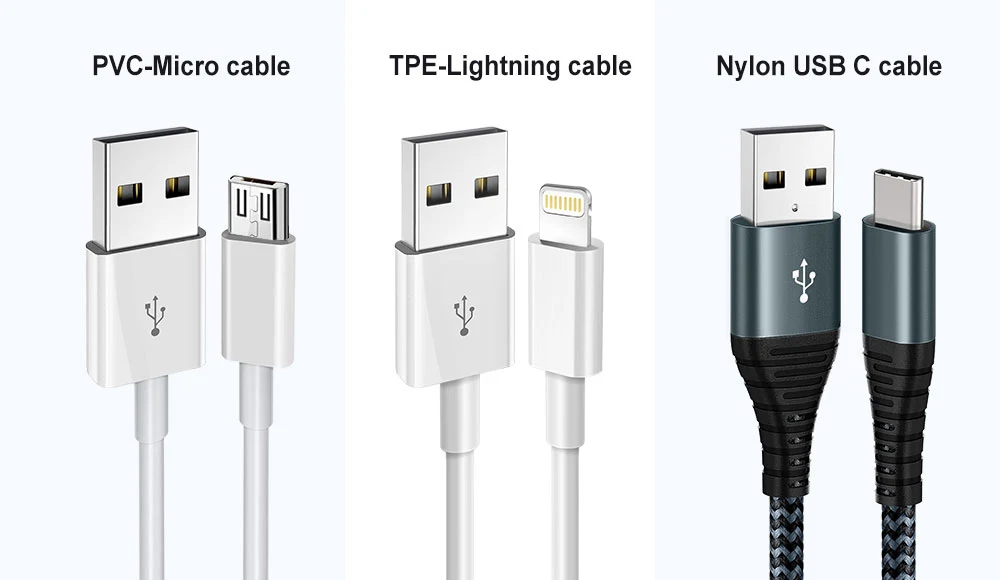
What are the types of USB cable jacket materials?
In the world of USB cables, the jacket material plays a key role, affecting the flexibility, durability and appearance of the cable. Below we will introduce three common cable jacket materials in detail: thermoplastic elastomer (TPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and nylon braid, as well as their characteristics and application scenarios.
- TPE:TPE cable jacket material is known for its superior elasticity and durability. This material is very soft, easy to bend and fold, suitable for mobile devices and charging scenarios. Its abrasion-resistant properties extend cable life, and its eco-friendly properties make it an eco-friendly choice.
- PVC: PVC is an affordable jacket material suitable for mass production. It has good insulation properties and can protect the inner wires from external interference. PVC has strong chemical corrosion resistance and is suitable for various environments.
- Nylon Weave: Nylon weave jacket material combines durability and stylish appearance. Its high strength allows the cable to withstand high tension and compression while reducing kink and tangle problems. The nylon braid also adds modernity and visual appeal to the cable.
What are the types of USB cable interface?
Different data cable interface options build interconnectivity between modern electronic devices. These small connectors can effectively help various devices to charge, transfer data and communicate with each other. Let’s go, let’s get to know the common ports on the data line together.
- USB-A port:This is the most common type of USB port, usually used for computers, computer peripherals, and chargers. It has a rectangular shape and is compatible with many legacy devices.
- USB-B port:It has a square shape and is usually used to connect a certain type of peripheral. USB-B ports are commonly found on external devices such as printers and scanners.
- USB-C port:USB-C is a full-featured, omni-directional connection standard. It is reversible and can be used for data transmission, video output and charging at the same time. Modern devices are increasingly adopting the USB-C interface cable.
- Lightning port:Introduced by Apple, the Lightning port is used for iPhone, iPad and other devices. It is small and reversible, supports high-speed data transfer and charging.
- Micro USB port: Micro USB is widely used in mobile devices, old cell phones and other external devices. Although it is gradually decreasing in new devices, it still has a certain market user base and is still used in some scenarios.
These small connection points pair different transport protocols and specifications to create a seamless bridge between devices.
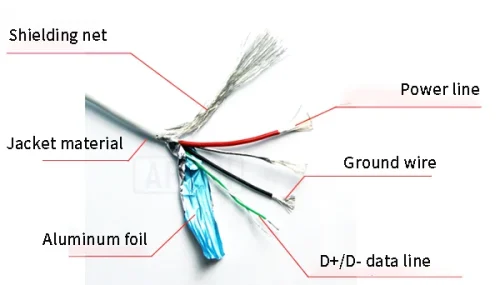
Comprehensive analysis of charging data cable structure.
The high-end USB data cable structure is usually composed of: outsourcing material – braided shielding net – aluminum foil – copper core. The innermost layer is covered with a colored insulating jacket material to transmit data signals and current, and the plastic shell is used to protect the wires; while the braided mesh and aluminum foil layer are used for shielding.
- The type of jacket material has been mentioned above, and it plays an important role in protecting the inner structure of the cable. This material acts as a shield in the external environment, protecting the wires from damage.
- Shielding net:Why do you need a shielding layer? It is because the current passing through the power cable is relatively large, or when transferring data at high speed, a magnetic field will be generated around the current. In order not to affect other components, a shielding layer is added to prevent the interference electromagnetic field from spreading outward, thereby ensuring the pure transmission of signals.
- Aluminum foil: The role of aluminum foil is the same as that of the shielding net. High-quality data cables must be wrapped with these two layers of media. At the same time, the aluminum foil also has a certain heat insulation effect.
- Copper core:There must be 4 connecting wires inside the standard data cable. They are not only responsible for transmitting data signals, but also undertake the task of current transmission. The materials of the wire core are respectively: iron core<iron core galvanized<iron core copper-plated<copper wire. The quality and material of the copper core determine the performance of the data line. Copper wire core material is the best choice because of its excellent data transmission capabilities.
Each connecting line is wrapped by insulating material (PE). In the past, the common core specifications in the market were 6 cores, 8 cores, and 10 cores in one line; now due to the development of electronic equipment, the cores have also been upgraded to 12 cores, 16 cores, and 24 cores. cores, 32 cores and 40 cores. More cores generally mean better performance, allowing more data and current to pass through.
In the internal structure of the data line, each part plays an integral role in ensuring the efficiency and reliability of data and power transmission. Therefore, when you pick up an APPHONE high-quality USB data cable, you can appreciate the mysteries of science and technology contained in it even more.
Learn more about USB cable wiring diagrams.
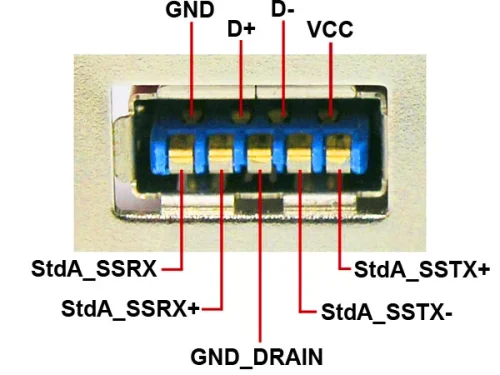
In the digital world, the wiring diagram of a USB cable is like a “picture book” of data transmission, which tells us how data flows from one place to another. How to wire according to the USB cable color code? For the male head of the USB port, the corresponding functions of the four contact pin arrays from left to right are:
- Ground wire (GND or GROUND):The color is usually black or brown, also known as the neutral wire. Like the earth, it provides a “home” for the entire circuit. Its function is to ensure that the potential of the circuit is stable, thereby ensuring the reliability of data transmission.
- Read the data line (Data+ or USB Port+):The color is usually green. It carries the data signal sent from the device, telling the receiving device “I have some data to send to you”. As a signal output line;
- Write data line (Data- or USB Port-):The color is usually white, as a signal input line. It receives data signals from other devices and acts like an ear for listening to information sent by other devices. These two data lines work together to ensure the smooth flow of information between devices.
- Power line (VCC or VBUS):Usually red in color, with +5V DC power supply, as the positive line of the power supply. This is like the “power source” of the USB cable, providing the power required by the device to ensure that the device can function and charge normally.
| USB Cable Wiring Guidelines Form | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| PIN | Name | Color | Description |
| 1 | VCC | Red | Power +5V |
| 2 | D- | white | data writing |
| 3 | D+ | green | data output |
| 4 | ID | none | A/B two interfaces; A: connected to the ground wire; B: Not connected to the ground wire; |
| 5 | GND | black | Signal Ground, Neutral |
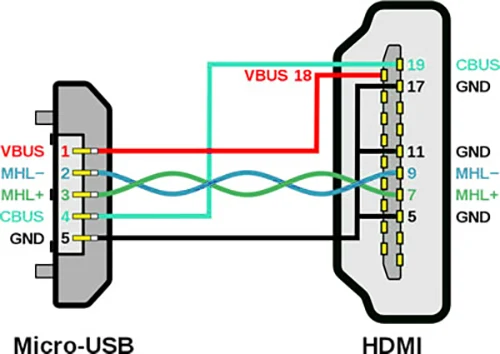
The principle of the Micro USB data cable wiring diagram is consistent with that of the USB wiring diagram. The figure below will take micro to HDMI cable as an example:
The USB TYPE C wiring diagram is also based on the 4-wire basic principle of the circuit, but because the number of pins is 24 pins, it needs to be classified and rationally wired. Due to the length of this article, if you want to know the USB C pin array and wiring diagram, please go to our corresponding professional blog to learn more.
In short, the USB cable structure is like a small workshop. Each component performs its own duties and cleverly connects electronics and information, allowing us to achieve seamless connection between different devices.
At APPHONE, we manufacture high-quality USB cables with outstanding professionalism to provide the best performance for your device. But that’s not all, we pride ourselves on the fact that our products are customizable. Whether you need a specific color, length, material, or other special needs, we have a solution for you. We understand that each client is unique, so we are committed to meeting your customization needs to ensure that your equipment is at its best in terms of performance and appearance.
If you are interested in our products and services, we welcome you to contact us at any time. Whether you are looking for a standard USB cable or a custom product with special needs, we have a dedicated team to support and consult you. Contact us now to start your USB cable customization journey, let us create the future of connection together!