What is Bluetooth Technology and Different Versions

We are now surrounded by technology and electronic devices 24/7. From Wi-Fi, NFC technology, and Bluetooth technology to devices like tablets and smartphones that you always carry with you. Each technology has different uses and characteristics and is developed based on the objectives and needs of companies and users.
In the year 2021, more than 4.7 billion Bluetooth® devices were shipped globally. As one of the most widely used wireless connectivity standards, Bluetooth technology has become an essential part of our daily lives. Therefore, this article will focus on Bluetooth technology, its different versions, and future aspects of Bluetooth technology.
What is Bluetooth Technology?
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless communication technology that allows devices to connect. This is the basic Bluetooth technology definition. This communication protocol appeared in the 90s and was developed by a consortium of companies including Ericsson, IBM, Toshiba, Intel, Nokia, and Sony. These companies recognized the potential of wireless technology and decided to invest in its development. It first appeared on the market in the 2000s, was integrated into many devices, and gradually gained success until it took its current Bluetooth version.
The basics of Bluetooth technology is it allows you to connect different types of devices up to 100 meters apart without cables. Furthermore, data is transmitted between devices thanks to radio frequencies operating in the ISM band. Today, Bluetooth is available on many devices, including tablets, PCs, smartphones, cameras, printers, and cars. All this makes it possible to exchange data and information and synchronize devices. For example, you can send documents, files, audio, etc.
Bluetooth technology operates on radio frequencies in the 2.4 GHz range. There are two Bluetooth standards currently in use today:
- Bluetooth Classic: supports two distinct data rates: Basic Rate (BR) and Enhanced Data Rate EDR.
- Bluetooth Low Energy (LE): which is optimized for low power consumption and is mainly used for applications that are constrained by battery life. Bluetooth LE is not commonly used to transfer large amounts of data but will offer support for higher audio streaming quality and more diverse listening options than Bluetooth Classic.
Bluetooth connectivity is easy to set up, available on almost all devices, and free. No special app or connection is required. Bluetooth technology continues to evolve with newer versions. Below are some key Bluetooth technologies in the newest Bluetooth versions.
Advance Bluetooth's Key Technologies You Should Know About.
Bluetooth uses several important technologies that work together to deliver this wireless functionality. Here are some of the foundational components that make Bluetooth current version of technology work.
EATT - Encryption and Authentication:
The Enhanced Attribute Protocol, or EAP, upgrades how Bluetooth devices exchange information between each other. Think of your phone as the “client” requesting data, and your earbuds as the “server” providing it.
EAP allows some really useful new features. For example, you’ll be able to simultaneously play audio from two apps like a game and a music player. Before this, Bluetooth could only handle one audio streaming at a time.
It’s also expected to reduce latency, the delay between sending and receiving data wirelessly. Faster data transfers mean audio and video should feel more in sync. However, EAP is optional for device manufacturers to implement. Not all Bluetooth 5.2 products may include it since it depends on what each company chooses to do.
LEPC - Low Energy Packet Configuration:
The Low Energy Power Control (LEPC) feature plays an important role in Bluetooth connectivity. LEPC allows paired devices to monitor the distance between each other using the Bluetooth signal. Maintaining an accurate sense of proximity is key, as it determines the optimal transmit power level needed for strong communication.
By keeping track of how far apart devices are, LEPC enables them to dynamically adjust their power output accordingly. Closer devices can reduce power while still maintaining a clear connection. This conserves battery life by using only as much power as required.
Knowing the distance also helps reduce interference and errors. At shorter ranges, devices can lower their power output to minimize signal bleed over to other nearby Bluetooth or WiFi connections. This decreases disruptions from wireless noise in dense environments.
LEPC further enhances stability by reducing feedback errors that can occur from devices being too far or signaling at an unnecessarily high power level. Connection drops, delayed responses, and other issues are less likely to happen thanks to precise distance monitoring.
Isochronous Channels:
The latest Bluetooth version 5.2 introduces Isochronous Channels, allowing multiple synchronous streams over a single connection. “Isochronous” means simultaneous transmissions – enabling exciting new ways to use wireless audio.
With Isochronous Channels, a single device like a phone can pair with multiple earbuds simultaneously. This solves persistent issues like one earbud disconnecting when taken out. Now both earbuds maintain an independent connection, and you can freely use one or both without interruption. Expect better audio separation for stereo content too.
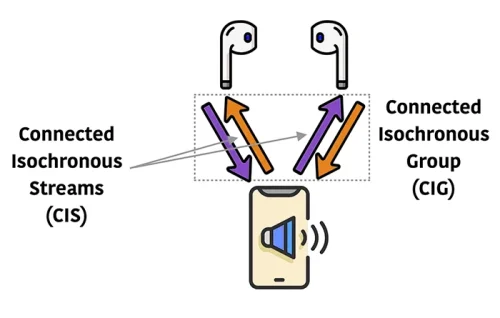
In addition to multi-streaming to individual devices, Bluetooth 5.2 allows a source to broadcast to many receivers at once. Your phone could synchronize music playback on multiple pairs of earbuds for shared listening. Public spaces may broadcast one audio signal to many hearing aids or speakers as well. The possibilities are promising!
Isochronous Channels overcome previous one-to-one limitations. Expect a more seamless experience jumping between audio sources, as well as emerging shared listening solutions with the Bluetooth version latest. While its full potential awaits device adoption, this new capability is poised to enhance how we experience wireless audio in many contexts. The future of on-the-go multimedia just got a worthwhile upgrade.
ADI Broadcast Data:
ADI (Alternate Data/Control/Channel) Broadcast Data technology in Bluetooth allows Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) devices to broadcast small packets of data to other devices without needing to establish a connection. This technology is particularly useful for applications like beaconing, where devices periodically broadcast information to nearby devices, such as smartphones, without requiring pairing or user interaction.
ADI Broadcast Data technology enables efficient data transmission in low-power scenarios, making it suitable for various Internet of Things (IoT) applications, location-based services, and proximity detection systems.
Features of Bluetooth Technology.
Bluetooth technology allows devices to communicate with each other without cables or wires. Bluetooth relies on short-range radio frequency, and any device that incorporates the technology can communicate as long as it is within the required distance. Bluetooth offers an integrated wireless solution that is small, energy-efficient, globally accessible, and affordable, making it ideal for a vast range of connected devices. Here are some features of Bluetooth technology:
- Compact and Easy Integration: Bluetooth modules are designed to be small and easily integrated into personal mobile devices, making them ideal for compact gadgets.
- Low Power Consumption: Bluetooth devices operate in various power modes, including active mode for normal use and power-saving modes like breathing, holding, and sleeping, conserving energy when not in active communication.
- Global Applicability: Bluetooth operates in the 2.4GHz ISM band, universally available worldwide without the need for individual country-specific licenses, simplifying global adoption.
- Voice and Data Transmission: Bluetooth supports simultaneous transmission of voice and data through circuit and packet switching, enabling efficient communication channels for voice calls and data exchange at various rates.
- Strong Interference Resistance: With the proliferation of devices operating in the ISM frequency band, Bluetooth utilizes frequency hopping spread spectrum technology, rapidly switching between 79 channels to mitigate interference from other devices like microwaves and WLANs.
- Peer-to-Peer Connectivity: Bluetooth devices can establish temporary peer-to-peer connections, with one device acting as the master initiating connections and others as slaves, forming basic networks known as piconets.
- Cost-Effectiveness: As Bluetooth technology becomes more widespread, the market offers a variety of affordable Bluetooth chips and modules, driving down overall costs for consumers.
- Open Standards: The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) makes all Bluetooth technical standards publicly available, allowing global manufacturers to develop Bluetooth products that adhere to interoperability standards, ensuring compatibility across devices.
So, all these amazing features of Bluetooth technology make it accessible and easy to use everywhere.
How Does Bluetooth Technology Work?
Devices connected in a Bluetooth network communicate with each other using ultra-high frequency (UHF) radio waves. These are electromagnetic waves with frequencies around 2.4 gigahertz (2.4 billion waves per second). UHF waves of different frequencies are used in microwave ovens, GPS systems and many other devices.
Bluetooth works by sending and receiving radio waves in a band of 79 different frequencies (channels) centered on 2.45 GHz. This band is reserved for use by industrial, scientific, and medical devices, and is separate from the frequencies used by radio, television, and cellphones. The low power of Bluetooth transmitters allows for short-range communication, which is one of the biggest advantages of Bluetooth technology. This short-range also makes Bluetooth more secure than wireless networks that operate over longer ranges, such as Wi-Fi.
To connect two Bluetooth devices, a pairing request is exchanged between them. Once the devices are paired, they can communicate with each other automatically. Up to eight Bluetooth devices can communicate at any one time, and they don’t interfere with one another because each pair of devices uses a different channel. To minimize the risks of interference from other electrical appliances and to improve security, pairs of devices constantly shift the frequency they’re using, a technique known as spread-spectrum frequency hopping.
When a group of two or more Bluetooth devices are sharing information, they form a kind of ad-hoc, mini-computer network called a piconet. One device acts as the overall controller of the network, while the others obey its instructions. Two or more separate piconets can also join up and share information, forming what’s called a scatternet.
On the other hand, Bluetooth LE works differently. You can also pair devices to establish trust between them, but this is not required for all product types. Bluetooth LE devices that need to be discovered send special messages (called packets) in a process called advertising. Advertising packages contain useful information about advertising media. Another suitable device finds the advertising device by looking for (listening to) advertising packets and selecting the packets from the suitable device. Scans typically only occur when triggered by the user, such as by pressing a button on a smartphone application. Typically, the user is shown the corresponding discovered device details and selects the device to connect.
Bluetooth peripheral devices (such as an activity tracker or smartwatch) connected to the same central device (such as a smartphone) form a building-wide personal area network (PAN) or piconet. Between the smartphone in your pocket and the watch on your wrist. Once a piconet is set up, its members hop onto a radio frequency together and communicate with each other and with other Bluetooth piconets operating in the same room or with devices using other wireless technologies such as Wi-Fi. interference can be avoided. Fi.
Bluetooth technology also learns which radio channels are working properly and which are experiencing interference, allowing it to dynamically avoid bad channels and only use channels that are free of interference. This process, called adaptive frequency hopping, allows Bluetooth devices to operate very well even in environments with large numbers of wireless devices.
Bluetooth Vs. Wlan: What's The Difference Between The Two?
Bluetooth works in a similar way to Wi-Fi by converting data to radio frequencies in the 2.4 GHz spectrum. But unlike Wi-Fi, which has a range of 50 meters indoors and twice as long outdoors, Bluetooth focuses on keeping transmit power low to conserve battery power and prevent radio interference with nearby devices. This is primarily because it is based on the principle of creating a Personal Area Network (PAN), also known as a piconet.

A typical consumer Bluetooth device has a transmission range of 10 meters and a total transmitted power of less than 2.5 milliwatts. This allows small peripherals such as wireless earphones and mice to operate wirelessly without draining limited battery power. The simple ad hoc (peer-to-peer) nature of Bluetooth connectivity also reduces electronic complexity and implementation costs, making it easier to connect devices with low-cost peripherals such as headsets and input devices.
While the widely used Class 2 Bluetooth devices have a range of 10 meters or more, the range of Class 3 Bluetooth radios is limited to up to 1 meter, primarily for portable applications. However, such Class 3 devices are currently very rare. Interestingly, while the Bluetooth specification for Class 2 devices requires a range of 10 meters or more, Class 1 Bluetooth devices used in industrial applications can communicate well beyond 100 meters when combined with powerful radios. You can extend the range.
At first glance, you might wonder why two different wireless standards are needed to connect mobile devices and peripherals. However, both Wi-Fi and Bluetooth have quite different use cases that justify their coexistence in the consumer electronics space. The main differences between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi are wireless range, power consumption, and network topology.
We also know that the Bluetooth protocol was designed primarily with ad hoc or peer-to-peer network topologies in mind. This makes sense since it’s designed to connect computers and mobile devices and to wireless peripherals. It is also designed to operate with a limited wireless connectivity range, resulting in significantly lower power consumption. This works well because devices that support the Bluetooth protocol are portable and located close to the host machine.
While wifi uses a hub network topology to create a wireless local area network suitable for homes and small offices. This is due to the emphasis on faster data transfer speeds and significantly longer ranges, not to mention the hardware complexity associated with operating larger networks with far more connected devices. is explained.
However, Bluetooth and Wi-Fi have additional features that blur the line between the two wireless communications standards. More recently, Bluetooth 5 and its various versions added limited mesh networking capabilities. Meanwhile, Wi-Fi is also challenging peer-to-peer connectivity through Wi-Fi Direct. So, we can say both are wireless communication means but with their differences. And there are advantages and disadvantages of Bluetooth technology as well as Wifi too. Here are some main differences between Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi.
| Quick Comparison of Differences Between Bluetooth vs W-Fi | ||
|---|---|---|
| Features | Bluetooth | Wi-Fi |
| Carrier Frequency | 2.4GHz | 2.4GHz, 5GHz, 6GHz |
| Specifications Authority | Bluetooth SIG | IEEE |
| Network Topology | Point-to-Point, Mesh, Broadcast | Hub, Mesh |
| Maximum Bandwidth | 3Mbps | 9.8Gbps |
| Typical Range | 1-30 meters | 46-92 meters |
| Typical Latency | 3-200ms | 150ms |
| Cost of Implementation | Low | High |
| Ease of Use | Simple | Complicated |
What Versions Of Bluetooth Are There?
There are now more than ten different Bluetooth versions, all of which are compatible with each other with the exception of the low energy (LE) 4.0 version. However, versions older than Bluetooth 3.0 are rarely used. Here is a detailed insight into various Bluetooth version differences and Bluetooth version history:
In 2021, Bluetooth 5.3, the Bluetooth current version was introduced, bringing significant improvements to the table. This latest version Bluetooth boasts a range of enhancements that make it faster, more secure, and more reliable than its predecessors. One of the most notable improvements in Bluetooth 5.3 is its expanded range. With a coverage area of up to 240 meters, it is ideal for use in larger spaces, such as smart homes, where a single Bluetooth hub can now cover the entire area.
In addition to its extended range, Bluetooth 5.3 also offers a significant upgrade in data transfer rates. It can now reach a theoretical maximum speed of 2 Mbps, which is double the speed of the previous version. This makes it an excellent option for streaming high-quality audio and video content without any lag or interruptions. With its array of features and enhancements, Bluetooth 5.3 represents a significant leap forward in wireless communication technology.
The Bluetooth version 5.2 was introduced by the Bluetooth SIG during the CES 2020, which was held in January 2020. This version was introduced into the market alongside the next generation of Bluetooth LE Audio. The most significant change made between Bluetooth 5.1 vs. 5.2 was that version 5.2 has Isochronous Channels (ISOC). Isochronous Channels support BLE devices with Bluetooth 5.2 or later, which acts as the base during the implementation of LE Audio. The other 3 features that come with Bluetooth version 5.2 are Enhanced Attribute Protocol (EATT), LE Power Control (LEPC), and Multi-Stream Audio.
Bluetooth 5.1 was unconfined in 2019. When Bluetooth 5.0 vs. 5.1 are compared, version 5.1 was the first to support the Mesh-based model hierarchy. Its main improvement areas are the Angle of Departure (AoD) and Angle of Arrival (AoA), GATT Caching, Periodic Advertising Sync Transfer, and Advertising Channel Index.
Bluetooth 5.0 was presented by Bluetooth SIG in 2016, although it was Sony in their product Xperia XZ Premium who first implemented this technology. Both Bluetooth 5 vs. 4.2 primarily focused on refining connectivity and experience of the Internet of Things (IoT), thereby offering a unified flow of data. Between Bluetooth 5.0 vs 5.1, the Bluetooth 5.1 range is a bit higher. Its main areas of improvement include Slot Availability Mask (SAM), extensions of LE Advertising, 2 Mbit/s PHY for LE, LE Channel Selection Algorithm #2, and long-range LE Long non-connectable advertising high-duty cycle.
Bluetooth version 4.2 was released in 2014, making it possible for the release of the Internet of Things (IoT). Its main area of improvement includes link-layer privacy that extends the policies for scanner filters, low energy secure connection that extends the length of Data packets, and version 6 of the Internet Protocol Support Profile (IPSP).
Bluetooth version 4.1 was released in 2013, improving the user experience further. This version enabled easy transfers of bulk data, allowed multiple simultaneous roles and co-existed with LTE. Other new features supported by this version include 11n PAL, minor duty cycle directed publicizing, partial time of discovery, L2CAP Connection, dual-mode and topology, LE link-layer topology, comprehensive interlaced scanning, a fast interval of data advertising, mobile wireless coexistence signaling services, and wideband speech from audio architecture updates.
Bluetooth 4 introduced a new wireless technology called Bluetooth Low Energy BLE, also known as Bluetooth Smart. BLE is designed for low-power devices that require long battery life, such as fitness trackers and smart home devices. It operates on a separate frequency band from classic Bluetooth and has a range of up to 50 meters.
In 2009, Bluetooth 3.0 + HS was released, and the key feature of this version was its high-speed data transfer. With the help of 802.11 Wi-Fi radio, it could reach data speeds of up to 24 Mbit/s, which was over 11 times faster than just three years prior. This version was able to transfer large amounts of data by using the 802.11 link for faster transmission while still using Bluetooth radio for discovery, connection, and configuration.
The use of Wi-Fi radio, in addition to the implementation of an enhanced power control feature, made it possible to efficiently use power. Even though using a Wi-Fi radio may require more power, it remains off most of the time until data transfer is required. The introduction of unicast connectionless data (UCD) also allowed this version of the device to be more responsive, while near-field communication (NFC) was also permitted.
In 2007, Bluetooth 2.1 was released, and the most important feature of this version was the implementation of Secure Simple Pairing (SSP). This system made the pairing process simpler and more secure, with required encryption for all connections making man-in-the-middle attacks more difficult. These attacks occur when third parties intercept and relay messages between two parties who think they are talking to each other directly. Lastly, the introduction of Extended Inquiry Response (EIR) enhanced the filtering of devices that appeared when scanning for connection.
In 2004, Bluetooth 2.0 + EDR was released, making it easier for people to use the technology in their everyday lives. The most notable feature of this version was the implementation of Enhanced Data Rate (EDR) technology, which theoretically allowed users to boost data transfer to a maximum of 3 megabits per second (Mbit/s). In reality, however, it could be boosted to 2.1 Mbit/s.
Bluetooth 1.2 introduced adaptive frequency hopping (AFH), which improved interference handling and reduced power consumption. AFH allows devices to hop between different frequencies more quickly and efficiently, which helps to avoid interference from other wireless devices. It also introduced new security features, such as encryption and authentication.
Bluetooth 1.1 introduced improvements to reliability and interoperability, although it was not entirely backward compatible with earlier versions of bluetooth. It added support for non-encrypted channels, which allowed for faster data transfer rates, and it improved the pairing process by reducing the number of steps required.
Bluetooth 1.0 was introduced in 1998 and was a significant breakthrough in wireless communication technology. However, due to its immaturity, it faced challenges such as a lack of anonymity. Although Bluetooth 1.1 fixed some minor issues, the major problems were addressed in Bluetooth 1.2, which introduced features such as adaptive frequency-hopping spread spectrum (AFH) for minimizing interference, faster transmission speeds of up to 721 kbit/s, Host Controller Interface (HCI), improved discovery, and Extended Synchronous Connections (ESCO).
Bluetooth 4 VS Bluetooth 5- What the Difference.
Bluetooth 5 is faster than Bluetooth 4 with the format having 2Mbps, twice the speed of Bluetooth 4 about 1 Mbps making Bluetooth 5 able to meet one of IoT requirements. This is thanks to the 5 Mbps bandwidth of the Bluetooth 5 in comparison to 2.1 Mbps of the Bluetooth 4. Both are widely used wireless communication technologies, but they have some key Bluetooth version differences that make them better suited for different applications. In this part of the article, we will compare Bluetooth 4 vs Bluetooth 5 in terms of their features, benefits, and applications.

Bluetooth 4.0: Features and Benefits
Bluetooth 4.0 was introduced in 2010 to be more power-efficient than previous different Bluetooth versions. Comes at High Speed (HS)’ Bluetooth 3, which enables fast data transmissions over Wi-Fi transports but at high energy consumption. One of the key features of Bluetooth 4+ is its long battery life, which means products using Bluetooth 4 can last up to three times longer compared with earlier Bluetooth versions. Another feature is the ability of Bluetooth 4.0 devices to operate in both single-mode and dual-mode functionality. This feature will provide backward compatibility.
Bluetooth 4.1, specified in 2013, extended the range of wireless connections so that more devices could be interactively linked, expanding the potential of Bluetooth for IoT and commercial applications, as well as enhancing the performance of consumer devices. Bluetooth 4.1 also helped further reduce power consumption while allowing two-way communication over rapid speeds, facilitating faster and more reliable transfers. Also, Bluetooth 4.1 has user-friendly features such as proximity pairing. With this feature users only needed to be in close range of a paired device instead of entering an access code or passkey.
Bluetooth 4.2, specified in 2014, brought several innovations to the communications standard that improved its applicability to Internet of Things applications. The protocol enabled greater interoperability between devices, higher encryption, faster speeds, and lower power consumption (through Enhanced Power Control, which allowed devices to save energy by quickly entering an idle state when appropriate), while also providing a better wireless range and more secure data transmissions. Up to eight Bluetooth Smart Ready controllers could now be grouped, allowing for the simultaneous transmission of data to multiple devices at once.
Bluetooth 5.0: Longer Range and Faster Speed
Bluetooth 5.0, specified in 2016, was developed to provide robust and reliable connections over longer distances than previous versions. For example, previous protocols could only reach a maximum of 33 feet, but with Bluetooth 5.0 this range has increased significantly to up to 300 feet in certain conditions, making it an ideal short-range wireless data transfer system for industrial applications. Bluetooth 5.0 also has double the speed of its predecessor, which allows faster data transfers from one device to another, making it an even more practical solution for commercial usage.
Bluetooth 5.1, specified in 2019, was a major update in Bluetooth technology, increasing the speed, stability, and range of Bluetooth LE connections, which can now be used for connecting proximity sensors and other IoT devices. Additionally, 5.1 supports Angle of Arrival (AoA) and Angle of Departure (AoD).
| Quick Comparison of Main Differences Between Bluetooth 4 VS Bluetooth 5 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Feature | Bluetooth 4 | Bluetooth 5 |
| Release Year | 2010-2013 | 2016-present |
| Maximum Range | Up to 33 feet | Up to 300 feet |
| Maximum Speed | 1-2 Mbps | 2 Mbps (double v4) |
| Battery Life | Long, up to 3x v3 | Further improved efficiency |
| Modes | Single and dual-compatible | Single mode only |
| Advanced Features | Proximity pairing; Enhanced power control | Longer range; Faster speeds; Angle of arrival/departure; |
| Applications | IoT, consumer devices | Extended-range IoT, industrial |
How to Check Bluetooth Version?
If you need to check the Bluetooth version installed on Windows 11 or 10 of your computer, you can quickly find out by following these steps:
- Step 1: Open the Device Manager by right-clicking the Start button and selecting Device Manager from the menu.
- Step 2: Expand the Bluetooth category by clicking on the arrow next to it.
- Step 3: Right-click on the Bluetooth adapter and select Properties from the context menu.
- Step 4: Click on the Advanced tab in the Properties window.
- Step 5: Under the Bluetooth Radio Information section, check the Firmware Version field and note the LMP (Link Manager Protocol) version number.
You can check the LMP version using the table below to determine the Bluetooth version on your computer.
| LMP | Bluetooth Version |
|---|---|
| 0 | Bluetooth 1.0b |
| 1 | Bluetooth 1.1 |
| 2 | Bluetooth 1.2 |
| 3 | Bluetooth 2.0 + EDR |
| 4 | Bluetooth 2.1 + EDR |
| 5 | Bluetooth 3.0 + HS |
| 6 | Bluetooth 4.0 |
| 7 | Bluetooth 4.1 |
| 8 | Bluetooth 4.2 |
| 9 | Bluetooth 5 |
| 10 | Bluetooth 5.1 |
| 11 | Bluetooth 5.2 |
| 12 | Bluetooth 5.3 |
Once you complete the steps, you will know the Bluetooth adapter version you have on your computer. If you find out that your device doesn’t have a specific version with a required feature, you can always get an inexpensive USB Bluetooth adapter from any reliable brand.
If you’re looking for a reliable and innovative brand for your wholesale hub adapter needs, consider APPHONE. At APPHONE, we specialize in developing multifunctional adapters that enable seamless connectivity for your business. Our research and development team is dedicated to creating innovative hub adapters with voltage surge protection, ensuring the safety of your electronic equipment by reducing the risk of overheating and overloading.
Choose APPHONE for your wholesale hub adapter needs and enjoy affordable prices, reliable products, and excellent customer service. Contact us today to learn more about our products and how we can help you meet your business needs.
What's Different About Bluetooth 5.3?

Bluetooth 5.3 is the latest version of Bluetooth and comes under the Bluetooth 5 umbrella. An incremental upgrade, Version 5.3 adds more stability, security, and efficiency. Peripherals can list preferred channels with a central device. Previously, only the central device could set channels.
Bluetooth 5.3 was first released in July 2021 before hitting the market in May 2022 and has since become available for a wide range of devices with wireless capabilities. Bluetooth 5.3 goes a step further and introduces further changes to the Bluetooth standard.
In comparison with its predecessor Bluetooth 5.2, Bluetooth 5.3 brings some significant enhancements. One notable addition is the support for two modes: Enhanced Data Rate (EDR) mode and Low Energy (LE) mode. EDR mode enables faster transmission speeds of up to 50 Mbps, while LE mode achieves a respectable 2 Mbps. Despite these advancements, Bluetooth 5.3 maintains the same transmission rate of 42 Mbps and a theoretical range of 300 meters as Bluetooth 5.2.
In terms of audio technology, Bluetooth 5.3 shines with its lower latency, enhanced anti-interference capabilities, and reduced power consumption compared to Bluetooth 5.2. These improvements greatly benefit gaming experiences, especially for users utilizing truly wireless headphones. With Bluetooth 5.3, the sound transmission delay is significantly reduced, surpassing the already impressive performance of many existing low-latency true wireless products on the market. This reduction in latency, coupled with enhanced anti-interference features, minimizes disconnections in challenging environments, resulting in an overall enhanced gaming experience. Now let’s have a look at the big changes that the newest Bluetooth version 5.3 brings.
- Periodic Advertising Enhancement
In the past, Bluetooth devices would send the same data multiple times to ensure it was received. Now, with Bluetooth 5.3, data is only checked once, saving energy for the receiving device. How does this work? A special part of the Bluetooth signal identifies if data has been received correctly or if it’s a duplicate. If it’s a duplicate, it’s discarded instead of being sent to the device. - Encryption Key Size Control Enhancements
Bluetooth 5.3 makes communication between devices more efficient by reducing the number of messages exchanged. Usually, Bluetooth uses encryption to protect the data being sent. The strength of this protection depends on the length of the encryption key. With this new feature, a device can specify the minimum key size needed, cutting down on unnecessary communication. This makes it faster for devices to agree on the level of security needed. - Connection Sub rating
Bluetooth devices have different modes for conserving power, like a low-power mode when not in use and a high-power mode when active, such as during a call or when playing music. Bluetooth 5.3 improves the transition between these modes, making the switch faster. This means a smoother experience for users, as their devices can respond quickly when needed. - Channel Classification Enhancement
With Bluetooth 5.3, devices can now better organize data sent over different frequencies. Previously, only the main device could do this. Now, both connected devices can work together to organize data, reducing the chances of data collisions and improving overall speed. This also helps maintain a stable connection, especially when devices are far apart.
| Quick Comparison Table of Bluetooth 5.0 vs. 5.1 vs. 5.2 vs. 5.3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bluetooth Version | 5.0 | 5.1 | 5.2 | 5.3 |
| Release year | 2016 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 |
| Data transfer | 2Mbps | No significant improvement | No significant improvement | No significant improvement |
| Communication range | 120 feet outdoor range | Improved indoor positioning accuracy to 1 cm. | No significant improvement | No significant improvement |
| New features | 255-byte message capacity | Enhanced Bluetooth LE Audio | EAT—more efficient data transfers, LC3 codec for improved audio quality, and CTKD for enhanced security | Channel Classification for reduced frequency interference and periodic advertising enhancements for better network efficiency |
Development Prospects of Bluetooth Technology.
Since its origins in wireless connectivity between devices, Bluetooth has transformed into a robust platform for whole-home and industrial networking through enhancements like Bluetooth Low Energy. The latest specifications unlock intriguing new avenues as well.
With positioning features such as Angle of Arrival, Angle of Departure, and distance measurement now within reach, Bluetooth is poised to deliver location services with centimeter-level precision. This cutting-edge capability could open up innovative automation scenarios.
Imagine if smart devices gained contextual awareness of their surroundings and each other, allowing for intelligent, autonomous responses based on real-time space sensing. Home appliances, locks and sensors coordinating seamlessly through adaptive mesh networking would take convenience and functionality to new levels.
Here are some key developments and trends to look out for:
- Bluetooth Low Energy (LE) Dominance: Bluetooth LE is expected to continue its growth, with 97 percent of all Bluetooth devices including Bluetooth LE by 2027. This low-power variant of Bluetooth is ideal for IoT devices, wearables, and other battery-powered devices.
- Auracast Broadcast Audio: Auracast is a new Bluetooth capability introduced as part of the Bluetooth LE Audio standard. It allows for personal sharing of audio streams with nearby devices, simultaneous audio transmission to multiple devices in public spaces, and multiple audio streams between Bluetooth devices. This technology opens up new possibilities for shared listening experiences in various settings.
- Lossless Audio Challenges: Bluetooth’s limited bandwidth has raised concerns about its ability to transmit lossless audio effectively. However, Bluetooth technology continues to evolve, and efforts are being made to address this limitation. For example, Apple has submitted a patent for optical audio transmission technology that can provide the required bandwidth for lossless audio.
- Power Consumption Efficiency: Bluetooth remains one of the most efficient short-range communication technologies in terms of power consumption. Features such as duty cycles, sleep mode, and connection sub-rating enable compact devices like wireless earphones to function effectively for extended periods.
- Regular Updates and Innovation: Bluetooth technology has undergone years of innovation and development, with regular updates to improve performance and connectivity. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) has reached version 5.3 in 2021, and Bluetooth Classic sees continuous improvements without the need for hardware replacement.
Of course, realizing the full potential of these emerging technologies will depend on creative implementations by manufacturers. But Bluetooth’s continuing evolution towards robust omnipresent connectivity lays a strong foundation for the next generation of spatial, interactive experiences. It’s an exciting time to see how industries may leverage these powerful new building blocks to shape the future.
We hope our article today gives you a good sneak peek into Bluetooth technology and Bluetooth technology history and future aspects. Bluetooth technology has become an essential component in our modern, interconnected lives. The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) is committed to advancing the technology and guiding its development into the future.
In the coming years, you can expect to see enhancements in Bluetooth technology, including increased range, performance, and reliability, as innovations are introduced. Bluetooth technology will continue to play a vital role in our ever-evolving wireless world. With its expanding use cases, Bluetooth technology will remain an integral part of our daily lives.
Who created Bluetooth technology?
Jaap Haartsen has been active in the area of wireless communications for more than 25 years. In 1994, he laid the foundations for the system that was later known as Bluetooth Wireless Technology, enabling connections between a seemingly endless array of devices.
What is the latest Bluetooth version?
Bluetooth 5.3. Bluetooth technology allows a wide range of consumer devices and commercial applications to connect wirelessly to other devices – and the field has seen many changes and developments over the past decade. At the time of writing (December 2022), the Bluetooth version latest is Bluetooth 5.3, which was specified in 2021.
Can I update my Bluetooth version?
Go to your Windows start button and find “Settings” Choose “Update & Security” Go to “Windows Update” and click on “Check for updates” which will scan for any updates and start upgrading automatically (if there is one available).
What is the working principle of Bluetooth?
Bluetooth uses a radio technology called frequency-hopping spread spectrum. Bluetooth divides transmitted data into packets, and transmits each data packet on one of 79 designated Bluetooth channels. Each channel has a bandwidth of 1 MHz.
What are the two types of Bluetooth technology?
The Bluetooth specification defines two types of links between Bluetooth devices:
- Synchronous, Connection-Oriented (SCO), for isochronous and voice communication using, for example, headsets.
- Asynchronous, Connectionless (ACL), for data communication, such as the exchange of vCards.
Why is called Bluetooth?
So what does it mean? Surprisingly, the name dates back more than a millennia to King Harald “Bluetooth” Gormsson who was well known for two things: Uniting Denmark and Norway in 958. His dead tooth, which was a dark blue/gray color, earned him the nickname Bluetooth.
What is the range of Bluetooth?
How far does Bluetooth usually reach? Commercial electronics, including most smartphones, headphones, earbuds, and portable speakers, fall into class 2, which gives them a range of about 33 feet. However, the maximum communication range will vary depending on obstacles (person, metal, wall, etc.) or electromagnetic environment.
What is a Bluetooth network called?
Bluetooth defines two types of networks: piconet and scatternet. PICONET: A Bluetooth network is called a piconet or small net.
Share This Artcle:

Fast delivery
Fastest delivery within 22 days

Quick proofing
Fastest 3-day proofing cycle

After-sale protection
24-month long warranty

1V1Customer Service
Professional customer service follow-up