What Is an Ethernet Port, Types, Uses and How Does it Work?

Have you ever looked at the back of your laptop, desktop, router, or other tech gear and seen those little square ports but had no idea what they were for? Well, those are Ethernet ports, and they play an important role in how all our devices connect to the internet connectivity and talk to each other.
Ethernet is a type of wired connection that allows electronics to communicate over a local network. Also, you may different types of Ethernet ports may look confusing at first, but once you understand their basics, they make a lot more sense.
In this guide, we’ll explain what Ethernet is, what are its different types, and how data moves between connected devices. Whether you’re setting up home wifi, troubleshooting slow speeds, or just curious about what all those mysterious ports do, this article covers the essentials of Ethernet in simple terms. So, let’s begin;
Read this blog to get the details about Different Types Of Connector Ports And Their Functions In Modern Devices.
What is An Ethernet Port?
An Ethernet port, also known as an Ethernet jack or socket, is an opening in networking hardware that Ethernet cables can be plugged into. The main purpose of Ethernet ports is to connect devices to a wired local area network (LAN) by using Ethernet cabling. This allows devices like desktop computers, laptops, routers, switches, IP phones, IP cameras, printers, and many other network devices to communicate and share network resources.
What Does An Ethernet Port Look Like?
An Ethernet port is a little wider than a phone jack. Because of this shape, it’s impossible to neatly fit an Ethernet cable into a phone jack, which makes it a little easier when plugging in cables. This is what an Ethernet port looks like. It’s a square with a couple of rigid areas at the bottom.
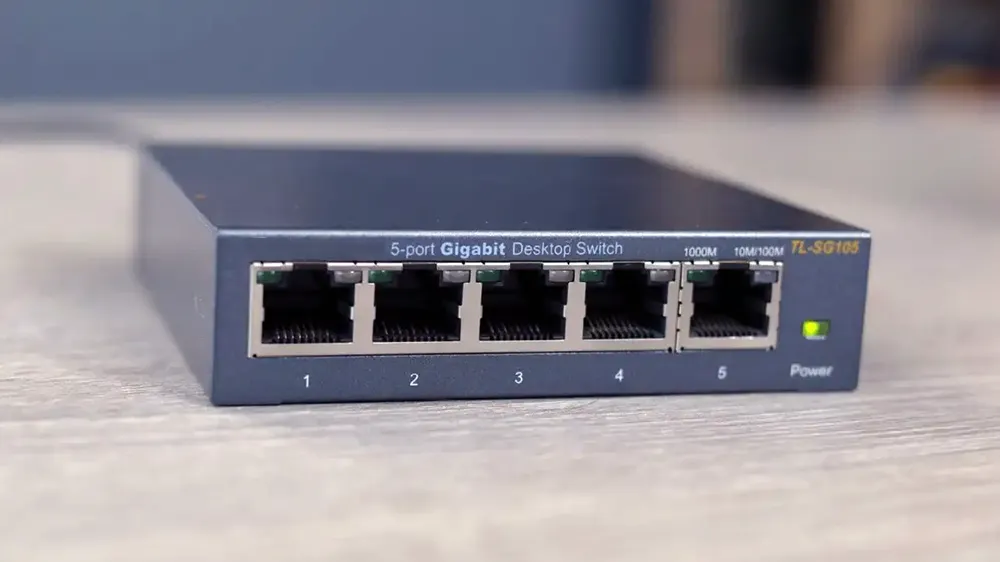
Ethernet ports are typically found on the back of desktop computers, laptops, routers, switches, and other networking equipment. Ethernet port computers and on these other devices enable wired connections between devices. Look at the image below It is a 6-port ethernet switch;
The standard port uses an RJ-45 connector to attach an Ethernet cable. RJ-45 refers to the registered jack-45 type of plug on the end of the cable. When plugged in correctly, the Ethernet cable’s clip fits securely into the bottom of the port to hold it in place. This provides a snug connection between the device and the cable.
The 7 Major Types Of Ethernet Cables.
There are seven categories of Ethernet cable in use today, offering various maximum bandwidth and data rates.
| Quick Comparison Table of 7 Major Types of Ethernet Cable | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ethernet Cable Type | Frequency | Maximum Speed |
| Cat5 | Up to 350 MHz | 100 Mbps |
| Cat5e (enhanced) | Up to 350 MHz | 1 Gbps |
| Cat6 | Up to 550 MHz | 1 Gbps |
| Cat6a (augmented) | Up to 550 MHz | 10 Gbps |
| Cat7 | Up to 600 MHz | 10 Gbps |
| Cat7a | Up to 1 GHz | 40 Gbps |
| Cat8 | Up to 2 GHz | 25 or 40 Gbps |
Now, Let’s find about each type in detail.
- Cat5:
Cat5 cables were among the earliest standards used for Ethernet networking. These cables support data transfer speeds of up to 100 Mbps and have a frequency range of up to 350 MHz. While Cat5 cables were once widely used for basic networking applications in home and small office environments, they have largely been surpassed by newer standards due to their limited speed and bandwidth capabilities. However, they may still be found in legacy systems or for applications where lower bandwidth requirements suffice. - Cat5e (enhanced):
Cat5e cables, an enhanced version of Cat5 cables, offer improved performance and reliability. With support for data transfer speeds of up to 1 Gbps and a frequency range of up to 350 MHz, Cat5e cables are widely used in modern Ethernet networks for faster and more reliable connectivity. They are suitable for a wide range of applications, including home networks, small office setups, and commercial environments where higher data transfer speeds are required. - Cat6:
Cat6 cables provide higher performance than Cat5e cables, with support for data transfer speeds of up to 1 Gbps and a frequency range of up to 550 MHz. These cables are ideal for high-speed networking applications and environments requiring greater bandwidth, such as streaming multimedia or large file transfers. Cat6 cables are backward compatible with Cat5 and Cat5e standards, making them a versatile choice for upgrading or deploying new networks. - Cat6a (augmented):
Cat6a cables, an augmented version of Cat6 cables, offer even higher performance and reliability. With support for data transfer speeds of up to 10 Gbps and a frequency range of up to 550 MHz, Cat6a cables are designed for demanding networking environments like data centers or commercial installations. They feature improved shielding and reduced crosstalk, providing superior performance and reduced interference for high-speed networking applications. - Cat7:
Cat7 cables offer higher performance than Cat6a cables, with support for data transfer speeds of up to 10 Gbps and a frequency range of up to 600 MHz. These cables feature advanced shielding and twisted pair design, providing superior performance and reduced interference for high-speed networking applications. Cat7 cables are ideal for environments requiring maximum performance and reliability, such as data centers or industrial settings. - Cat7a:
Cat7a cables are an advanced version of Cat7 cables, capable of supporting data transfer speeds of up to 40 Gbps and a frequency range of up to 1 GHz. These cables feature enhanced shielding and are ideal for high-speed networking applications requiring maximum performance and reliability. Cat7a cables are commonly used in demanding networking environments like data centers or commercial installations where ultra-high-speed connectivity is essential. - Cat8:
Cat8 cables are the latest standard in Ethernet cabling, offering blazing-fast data transfer speeds of up to 25 or 40 Gbps and a frequency range of up to 2 GHz. Designed for use in data center environments or other high-performance networking applications, Cat8 cables provide the highest level of speed and reliability. They are ideal for environments requiring ultra-fast networking speeds and can support a wide range of applications, from high-speed data transfers to multimedia streaming and online gaming.
Click to learn about data transfer GB, Gbps, Bytes to MB Formula Conversion Guide.
What Is An Ethernet Port Used For?
An ethernet port, also known as an ethernet jack, allows you to connect your computer to the internet via an Ethernet cord. Now let’s find out the functionalities and advantages of an Ethernet port, a key component in modern networking technology today.
- Transfer Files Between Two Computers: One of the primary uses of an Ethernet port is to facilitate the transfer of files between two computers. By connecting an ethernet cable with both devices, users can establish a direct and high-speed connection for seamless file sharing. This method is particularly useful in business settings where large files need to be exchanged quickly and efficiently.
- Equipped On A USB Hub Adapter: Another common use of an Ethernet port is when it is equipped with a USB hub adapter, allowing users to connect their computers to a network even if they do not have a built-in Ethernet port. This enables individuals to access the internet and share files across multiple devices without the need for a dedicated network card.
Read this blog to know about What is a USB Ethernet Adapter, and How Does It Work. - Connect To A Electronic equipment Without WiFi: Ethernet ports can also be used to connect devices that do not have WiFi capabilities, such as smart TVs or game consoles, to a network. By using an Ethernet cable, users can establish a stable and reliable connection that is often faster and more secure than wireless alternatives. This is particularly beneficial for streaming high-definition content or online gaming.
How to Transfer Files from PC to PC Using Ethernet Cable?
Now that you know about all the uses of ethernet cables, let’s delve into the file transfer process from PC to PC. Follow these steps:
Setting Up the LAN Network:
Before initiating the file transfer, establish a LAN network between the targeted devices using a suitable LAN cable, such as CAT5. Here’s how:
- Step 1: Connect the targeted devices with the LAN cable.
- Step 2: Enable the sharing option on both devices. Access the control panel from the device’s main menu.
- Step 3: Within the control panel window, navigate to “Network and Internet” and then select “Network and Sharing Center.”
- Step 4: In the subsequent window, choose “Change advanced sharing settings.” Adjust the following options:
1.Turn on network discovery.
2.Turn on file and printer sharing.
3.Turn on sharing so anyone with network access can read and write files in the Public folders.
4.Turn off password-protected sharing
5.Ensure to save all changes by clicking ‘Save changes’ on both devices.
Now Time to Initiate File Transfer:
With the sharing options activated on both devices, proceed with the file transfer process:
- Step 1: On the source device, select the desired folder for transfer. Right-click the folder, choose “Share with,” and then select “Specific people.”
- Step 2: In the ensuing file-sharing window, select “Everyone.” Click “Add,” followed by “Share” to proceed.
- Step 3: Once the folder is shared, click “Done” to confirm the action.
- Step 4: Now it’s time to ensure access to the shared folder on the destination device. Simultaneously press the Windows key + E to open the file explorer. In the file explorer window, select the “Network” option.
- Step 5: From the list, navigate to the source computer and double-click on it. If prompted, enter the password of the source computer.
Step 6: Upon successful access, locate the shared folder on the destination computer. Copy the folder to another location as needed.
And that’s all with these simple steps your files are transferred from one PC to another with a pc ethernet port.
How To Connect Ethernet Cable To Laptop Without Ethernet Port?
If your laptop doesn’t have a spot to plug in an Ethernet cable, don’t worry! You can still connect it using something called an adapter. Here’s how:
Ethernet Adapter for USB Type-C:
If your laptop has a small, oval-shaped USB port (that’s probably a USB Type-C port), you’ll need an Ethernet adapter for Type C that lets you plug in an Ethernet cable. You just connect one end of the cable to the adapter and then plug the adapter into your laptop’s USB port. It’s pretty straightforward and usually doesn’t need any special software to work. This works for both regular laptops and Apple ones.
Looking for a reliable USB-C to Ethernet adapter? Look no further than APPHONE! Our innovative technology provides instant internet access with speeds up to 5 Gbps, all in a seriously compact and portable design. Join the 50 million+ people already powered by our products, and experience the advantages of USB-C technology today. Plus, with our worry-free 12-month warranty and friendly customer service, you can trust that you’re making a smart investment.
Ethernet Adapter for USB Type-A:
If your laptop has regular rectangular-shaped USB ports (those are USB Type-A ports), there are adapters for those too. You just plug one end of the ethernet cable port into the adapter and then stick the adapter into your laptop’s USB port. Again, no fancy software is needed.
There are lots of these adapters out there, so you can pick one that fits your laptop and your budget. Just look for one that matches the type of USB port your laptop has to connect ethernet through USB port and you should be good to go!
How To Connect An Ethernet Cable To a TV Without an Ethernet Port?
If your TV doesn’t have an Ethernet port, it might not be able to connect to the internet or access streaming apps directly. But don’t worry, you can still get it connected with a few extra steps.
First off, you’ll need an external device to help your TV get online. One option is to connect your laptop to your TV using an HDMI cable. Another option is to use your phone, along with the right cable and adapter, to connect it to your TV.
Another option is to get an Apple TV box. This nifty little device turns any regular TV into a smart TV. Just connect the Apple TV to your Wi-Fi network, plug it into your TV’s HDMI port, and you’re good to go.
If your smart TV doesn’t have an Ethernet port, you can use a USB ethernet adapter. But be aware, that not all smart TVs support adapters, so it’s a good idea to check the user manual first to see if your TV is compatible.
Once you’ve got your adapter, just plug it into your TV’s USB port. Then, connect one end of the ethernet cable port to the adapter and the other end to your Wi-Fi router. And that’s it! Your TV should now be connected to the internet connectivity and ready to stream your favorite shows and movies.
What Is Ethernet Port Aggregation?
Ethernet port aggregation, also known as link aggregation or port trunking, is a networking technique that combines multiple physical Ethernet ports into a single logical port. This grouping of ports creates what is called a Link Aggregation Group (LAG). The primary purpose of Ethernet port aggregation is to increase both the bandwidth and the reliability of network connections.
By aggregating multiple physical ports into a single logical port, Ethernet port aggregation allows for a greater volume of traffic to be transmitted and received by the network simultaneously, resulting in increased throughput. This can be particularly beneficial in environments where high bandwidth demands are common, such as data centers or enterprise networks.
One key advantage of Ethernet port aggregation is its ability to enhance network reliability. If one of the physical ports within the LAG fails, the remaining ports can continue to function, ensuring uninterrupted network connectivity. This redundancy helps minimize downtime and ensures continuous operation, making Ethernet port aggregation valuable for mission-critical applications. Here are some of the advantages and disadvantages of ethernet port aggregation.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased Bandwidth | No Improvement in Download Speed |
| Redundancy | Limited Impact on Internet Speed |
| Cost Savings | No Routing Capability |
| Improved Network Performance | |
| Enhanced Reliability |
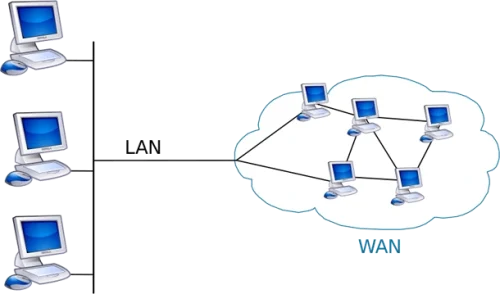
What Is The Difference Between An Ethernet Interconnect Local Area Network (Lan) And A Wide Area Network (Wan)?
LAN (Local Area Network) and area network WAN are two types of networks used for interconnecting computers, each serving different purposes and covering different areas.
LANs use local connections like ethernet cables and wireless access points. WANs use wide area connections like MPLS, VPNs, leased lines, and the cloud. LANs are faster because they span less distance and have less congestion. WANs are slightly slower, but that may not be perceived by your users.
LAN, or Local Area Network, is designed for smaller, localized networking environments such as homes, offices, or schools. It typically consists of computers and devices within proximity, connected via Ethernet cables or wireless cards to a common router or switch. LANs are known for their high speed, reliability, and security. They are commonly used for file sharing, printing, and resource sharing within a limited geographic area.
On the other hand, WAN, or Wide Area Network, covers larger geographic areas such as cities, states, or even nations. WANs connect multiple LANs over longer distances, often using public networks like the Internet or leased lines provided by telecommunications providers. WANs enable widespread connectivity but may have lower speed and reliability compared to LANs due to the extended distances involved.
Here’s a comparison of LAN and WAN:
| Aspect | LAN (Local Area Network) | WAN (Wide Area Network) |
|---|---|---|
| Stands For | Local Area Network | Wide Area Network |
| Coverage | Local areas (e.g., homes, offices, schools) | Large geographic areas (e.g., cities, states, nations) |
| Definition | Covers a small geographic area, such as a home or office | Spans a broad area, crossing metropolitan or national boundaries |
| Speed | High speed (typically up to 1000 Mbps) | Lower speed (typically up to 150 Mbps) |
| Data Transfer Rates | Higher data transfer rates | Lower data transfer rates compared to LANs |
| Example | Network in an office building | The Internet |
| Technology | Primarily Ethernet and Token Ring | Technologies like MPLS, ATM, Frame Relay |
| Connection | Can be connected via telephone lines or radio waves | Connected through public networks or leased lines |
| Ownership | Owned and managed by a single organization or person | Distributed ownership and management over long distances |
| Set-up Costs | Relatively inexpensive to set up | Higher set-up costs, especially for remote areas |
| Geographical Spread | Small geographical range | Large geographical range |
| Maintenance Costs | Easier to maintain at lower costs | Maintenance may be more challenging due to wider coverage |
| Bandwidth | High bandwidth available for transmission | Lower bandwidth available for transmission |
| Congestion | Less congestion | More congestion |
How To Test If An Ethernet Port Is Working?
Testing, if a laptop ethernet port is working, is like checking if a door is open or closed. The easy test is to turn on your computer and connect it to the jack with an Ethernet patch cord. You can then check whether the Ethernet port is working by:
- Check the Cable: Make sure the cable is plugged in snugly at both ends, like connecting pieces of a puzzle.
- Try Another Device: If you can, connect the cable to another device like a different computer or a router. This helps see if the problem is with the device or the cable.
- Look for Lights: See if there are any small lights near your laptop Ethernet port. A green light usually means everything’s good to go!
- Check Settings: Make sure the computer ethernet port is set up to use. It’s like making sure the car knows which road to take.
- Ping Test: This is like sending a message to see if anyone’s home. Open a special window on the computer and type a message to the network. If you get a reply, it means the connection is working.
- Use a Different Cable: If you have another cable that you know works, try using it. Sometimes the cable can be the problem.
- Update Drivers: Sometimes, the computer needs a little update. It’s like giving it a tune-up to work better.
- Check for Damage: Look closely at the Ethernet port to see if anything looks broken or dirty. If it does, clean it carefully.
- Try Another Port: If you’re connecting to a big box like a router, try plugging into a different hole. Sometimes one hole doesn’t work, but another one does.
- Reset Settings: If you’ve changed any settings, you can always go back to the way things were before. It’s like hitting a reset button to start fresh.
Following these steps should help you figure out if your Ethernet port is working or if there’s something else going on.
How To Fix An Ethernet Port?
If it’s ethernet port not working, there is how to fix an ethernet port;
- Sometimes, the cable might not be plugged in properly. Ensure it’s securely connected at both ends. Even a slight disconnect can cause problems.
- Just like how a good night’s sleep can refresh you, restarting your computer can sometimes fix connectivity issues. Give it a try!
- Cables, although rare, can sometimes go bad. Try using the cable with a different port or another device to see if it’s the culprit.
- If none of the above works, you may need to contact your electronic device manufacturer’s support team or your local network installer.There could be a hidden setting causing the problem that they can help you with.
By following these steps, you can hopefully get your ethernet port not working functionally and running smoothly again!
Ethernet ports have become ubiquitous in modern networking devices. They offer a reliable and efficient way to connect multiple devices using an ethernet cable. Whether it’s your computer, router, modem, game console, or streaming device, ethernet ports provide a fast and stable connection.
If you need a customized Ethernet adapter and cable solution, look no further than APPHONE. Our expertise in Ethernet HUB adapters allows us to provide you with a product that meets your specific needs. Whether you require a unique appearance, multiple ports, or different connection port types, we have the capabilities to make it happen. Trust us to deliver high-quality, reliable products that will enhance your network connectivity. Choose APPHONE for all your Ethernet adapter and cable needs.
Can the Ethernet port transfer files?
You can transfer files from PC to PC in various ways, such as through a USB flash drive, external hard drive, cloud storage service, email, Wi Fi, or an Ethernet cable. You can use an Ethernet cable or LAN cable to migrate files between two computers: When you don’t have access to a wireless network.
Does HDMI port support ethernet?
HDMI and Ethernet are two data transmission cables that cannot be more different. HDMI transmits audio and video signals, while ethernet cables transmit regular data. However, there is HDMI with Ethernet, a cable combining both features for multimedia purposes.
Does the laptop have an ethernet port?
Today, however, it’s uncommon to see Ethernet ports. They’re pretty large, which doesn’t lend itself to the smaller, thinner designs of modern laptops, and current Wi-Fi speeds are more than enough for most needs, so most laptops don’t come with an Ethernet port.
What is the difference between 100M and Gigabit Ethernet ports?
Gigabit switches and fast ethernet switches set the main difference here. Gigabit switches can transmit data at a rate of up to 1,000 Mbps, while 10/100 ethernet switches operate at a maximum speed of 100 Mbps. This means gigabit switches are ten times faster than fast Ethernet switches.
What is an Ethernet port used for?
An ethernet port, also known as an ethernet jack, allows you to connect your computer to the internet via an Ethernet cord.
What is Ethernet and how does it work?
Ethernet is defined as a networking technology that includes the protocol, port, cable, and computer chip needed to plug a desktop or laptop into a local area network (LAN) for speedy data transmission via coaxial or fiber optic cables.
What are the types of Ethernet?
Currently there are seven categories of Ethernet cable on the market: CAT5, CAT5E, CAT6, CAT6A, CAT7, CAT7A, and CAT8.
Which Port for Ethernet?
These ports, both on the router and on the end devices, are called Local Area Network (LAN) ports. They are also known as RJ45 ports or Ethernet ports. The moment you plug a device into a router, you have yourself a wired network. Networking devices that come with an RJ45 network port are called Ethernet-ready devices.
What is the full form of Ethernet?
The full form of Ethernet is “Ethernet local area network standard”. Ethernet supports a variety of data transfer rates, including 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, and 1 Gbps, and can support up to 10 Gbps in recent developments.
Share This Artcle:

Fast delivery
Fastest delivery within 22 days

Quick proofing
Fastest 3-day proofing cycle

After-sale protection
24-month long warranty

1V1Customer Service
Professional customer service follow-up