What is the Role of DAC Noise Reduction Chips
Ever wonder how your headphones or speakers output such clear, pristine audio? It’s likely thanks to a little chip called a DAC noise reducer. As digital music files are converted to analog signals, a tiny amount of unwanted static or hiss can be introduced. But DAC noise reduction chips help eliminate this using advanced algorithms.
By combing through the audio waveform, these chips can identify low-level noise and remove it without affecting the actual music quality. This results in a much “blacker” background and an overall cleaner, more lifelike listening experience. Music and voices really come through with impressive clarity and detail. If you’ve ever noticed a subtle “ssshhh” even at low volumes, a DAC noise reducer is probably helping minimize it.
In our today guide, let’s take a closer look at how these noise canceling chips work their magic to deliver pristine digital to analog conversions.
What is a DAC (Digital-to-Analog Converter)?
Ever wonder how your headphones or speakers are able to play back music with such clarity? It all comes down to a little component called a DAC, or digital-to-analog converter. You see, when we listen to digital music files, there’s an important behind-the-scenes step where the numeric digital code gets turned back into an actual sound wave our ears can understand.
That conversion from 1s and 0s to an instantly recognizable song is what a DAC handles. It takes the binary data and does the math to reconstruct the original analog waveform in as high-fidelity a way as possible. But not all DACs are created equal – the quality can really impact how clean and detailed the music sounds. Some even have adjustable settings so you can tweak it to your preference.
While the DAC inside a phone or tablet gets the job done for basics, an audiophile knows it won’t release your favorite tunes to their fullest potential. That’s where an external DAC shines – it can bring your favorite songs to life with a level of clarity and nuance you never thought possible from your device. If you want your music to soar without any technical limitations getting in the way, a premium standalone DAC is a must-have upgrade. It’s the key to hearing all the intricacies the artists put into each note and really immersing yourself in your favorite songs.
Importance of Digital-to-Analog Converters.
For musicians and music lovers alike, the journey of a song is truly incredible. It begins as mere vibrations, captured by delicate microphones as sounds float through the air of a recording studio. In those early days, engineers had to painstakingly transfer each analog waveform onto reels of magnetic tape to preserve it for the future. Meanwhile, listeners experienced music most directly through the magic of vinyl records, where grooves transformed back into songs under a spinning needle.
How times have changed! Nowadays, artists create digital empires of 1s and 0s rather than tangible tapes. But to bring these numeric files back to life, a secret weapon exists – the digital-to-analog converter, or DAC. You see, without this ingenious little chip, all our curated playlists would remain trapped as cold code. But the DAC performs its subtle magic, translating the numerical language of computers back into smooth, living curves that fill our homes with heartfelt harmonies once more.
Of course, not all DACs are equal. Just as musicians polish their craft, so too must audio engineers refine the reproduction process. Many audiophiles understandably seek the highest fidelity, choosing external DACs that uncover nuances hidden by basic sound cards. In doing so, the experience comes full circle once more – only this time, the songs sound more vibrant than ever before, letting us feel every emotion as if we were there in the studio ourselves. Truly, DACs are the gatekeepers of sound, bridging our digital and analog worlds with finesse.
What Is the Role of a DAC Chip in Audio Cables?
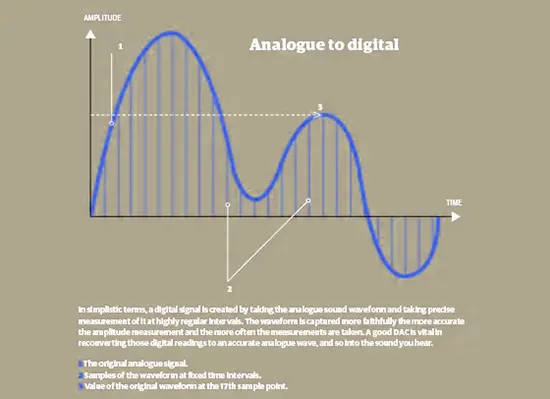
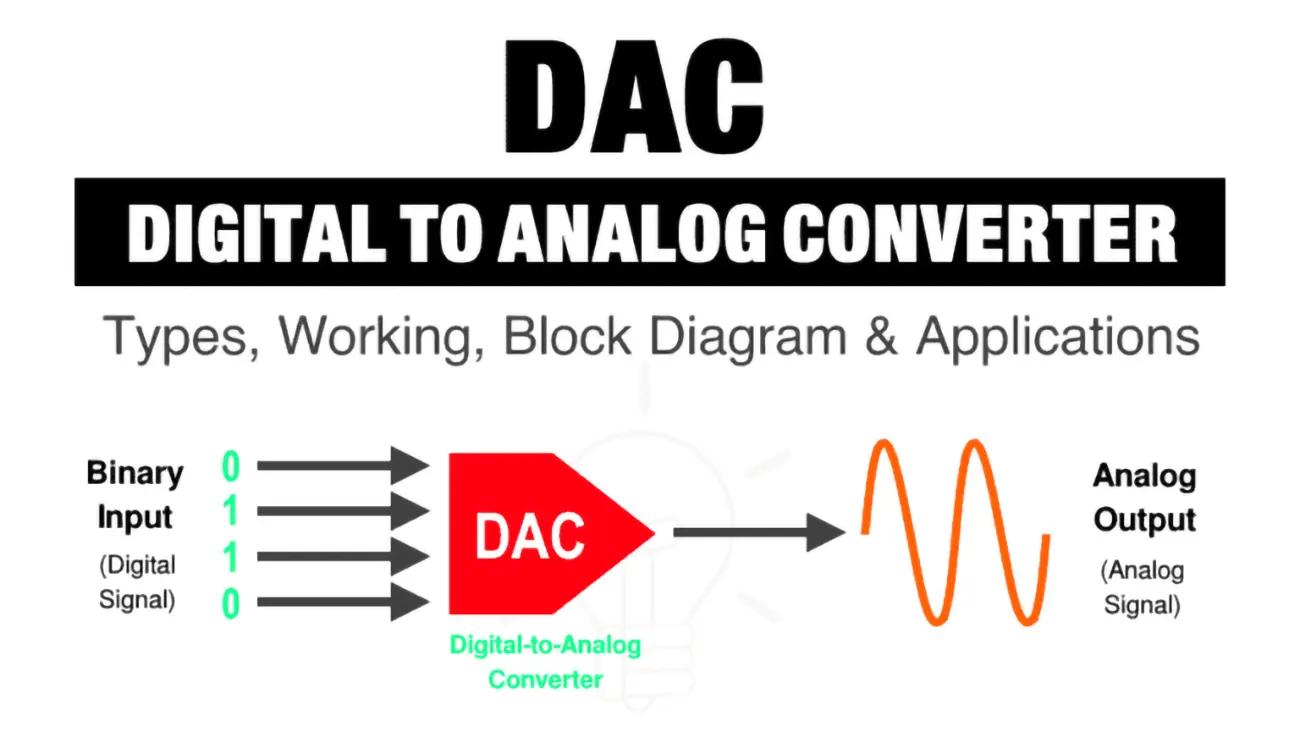
A DAC takes the jagged digital data & transforms it into an analogue electrical signal that your amplifier can then convert into smooth sound waves. Every time you listen to digital music through an analogue device (e.g. a pair of headphones) you’re using a DAC. This little component lives inside your cables and acts as a translator, taking all that binary data and converting it into an actual changing electrical signal. It works by sampling those digitized music files millions of times a second at a precise rate, like 44.1kHz, and outputting the corresponding voltage levels.
Those analogue waveforms can then be passed to your amp or headphones to faithfully recreate the music. The better engineered the DAC is, the more it can maximize the integrity of the original performance during this digital to analog process. Features like low jitter and high bit depth help retain fine detail and dynamic range.
So next time you’re jamming out, send some love to the underappreciated DAC chip making it all possible. Without it transforming those 1s and 0s behind the scenes, your tunes would just be incomprehensible code. It’s the real MVP in bringing your playlists to life.
How Do DAC Chips Improve Audio Quality?
Standalone DACs, especially high-end models, employ superior components, advanced circuitry, and more robust power supplies. This results in better sound quality, improved dynamic range, lower noise floor, and more accurate conversion of the digital signal to analog. In general, these chips significantly enhance audio quality by minimizing various types of noise that can degrade sound performance.
Types of Noise Affecting Audio Signal
- Quantization Noise:
Digital audio is sampled and quantized into discrete values based on the bit depth. The limited number of values can introduce quantization errors, leading to a grainy or harsh sound. For instance, lower bit depths (e.g., 16-bit) can result in noticeable noise in quieter passages of audio. - Jitter Noise:
Jitter refers to timing variations in the digital signal’s clock during sampling. These timing errors can cause misalignment in the audio waveform, resulting in distortion and loss of clarity, particularly in high-frequency sounds. - Power Supply Noise:
Variations or fluctuations in the power supply can introduce noise into the audio signal. This noise can manifest as audible hums or distortions, especially if the power supply is not well-regulated or filtered. - Electromagnetic Interference (EMI):
External electromagnetic fields can induce unwanted noise in audio circuitry, leading to interference that can degrade audio quality. This can happen due to nearby electronic devices or poor grounding practices.
How does a DAC chip work?
A DAC converts digital data into an analog audio signal, which it then sends to an amplifier. When you play digital recordings, you are actually hearing an analog signal that has been transformed from digital by the DAC.
Share This Artcle:

Fast delivery
Fastest delivery within 22 days

Quick proofing
Fastest 3-day proofing cycle

After-sale protection
24-month long warranty

1V1Customer Service
Professional customer service follow-up