What is Fast Charging: Principles and Standards Explained
on the same principle as standard charging, but with higher electrical power (amperage) transferred through the cable. Unlike standard chargers, fast chargers deliver a higher voltage ranging from 2 volts to 4.2 volts, resulting in a significantly faster charging rate.
In common the fast charging principle is based on the concept of delivering a higher current to the device being charged, enabling it to charge at a much faster rate. This is achieved through technological advancements in charging protocols, power delivery, and hardware optimization.
In today’s fast-paced world, where time is of the essence, the need for efficient and rapid charging has become paramount. The fast charging principle has revolutionized the way we charge our devices, providing a convenient and time-saving solution. This article will delve into the intricacies of this principle, exploring its benefits, working mechanism, and how it has transformed our charging experience.
How Many Watts is Considered Fast Charging?
Fast Charging has become a common term in the realm of chargers and devices, indicating the ability to charge faster than the standard 5 Watts. However, there is no universal industry language or standard to define fast charging technologies. USB 3.1 Power Delivery, commonly known as “Fast Charge,” allows for charging devices at up to 100~240W. This enables significantly faster charging speeds, allowing your phone to charge 2-4 times quicker. With Fast Charge, you can expect to reach a 50~80% charge in just 30 minutes.
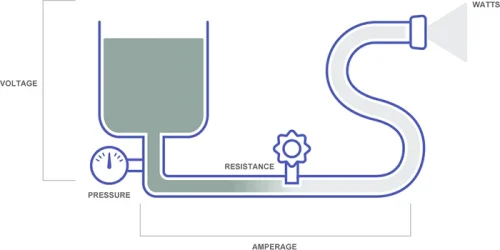
It’s important to note that not all products claiming fast charging capabilities deliver on this promise, often providing only the standard 5W charging speed. Fast charging relies on amperage, voltage, and watts. Amperage represents the amount of electricity flowing, voltage denotes the strength or speed of the current, and watts are calculated by multiplying amperage and voltage. A helpful analogy is comparing it to a watering hose, where amperage is the hose width, voltage is the water pressure, and watts indicate the water flow rate.
Charging occurs in two phases. Initially, higher voltage facilitates faster charging. Fast charging chargers optimize this phase to increase power delivery. As the battery nears full capacity, the charger reduces voltage to prevent overheating and overcharging, ensuring safety for both the device and charger.
To embark on a fast charging journey, ensure that your device, charger, and cable support the same fast charging standard. Some devices may require specific compatibility between the cable and charger. Additionally, take note of the maximum charging speed supported by your device and charger. For instance, if you use a 27W charger with a smartphone capable of a maximum charging speed of 18W, the phone will charge at 18W.
The Principle of Fast/Quick Charging.
Fast charging operates on the same fundamental principle as standard charging. However, the key difference lies in the higher electrical power (amperage) that is converted and transferred through the charging cable compared to a standard charger. In comparison, a standard adapter typically operates within a voltage range of 2 volts to 4.2 volts, resulting in a relatively lower electrical transfer rate.
To comprehend fast charging standards, it’s important to grasp the fundamentals of battery charging. Batteries have specific voltage requirements and can handle a certain amount of current for input and output. Higher voltage and current translate to more power and faster charging. However, batteries have strict operational limits, especially regarding voltage, which must be adhered to for safe charging.
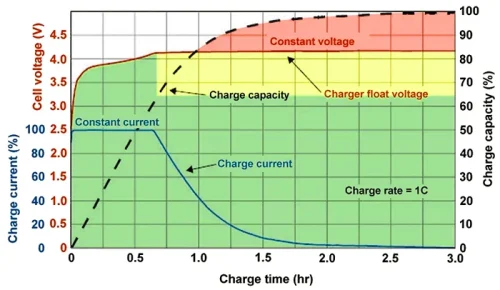
Fast charging does not simply involve applying the maximum possible voltage and current to a battery. Instead, battery charging consists of two distinct phases: constant current and constant voltage. The diagram below illustrates how voltage changes during charging and its impact on the current that can be delivered to the battery.
Fast charging technologies take advantage of the constant current phase by delivering as much current as possible to the battery before it reaches its peak voltage. As a result, fast charging is most effective when the battery is less than 50% charged, but its impact on charging time diminishes once the battery surpasses 80%. It’s worth noting that the constant current charging phase is less detrimental to the long-term health of the battery, as higher constant voltage and heat have a greater negative effect on battery life.
Manufacturers employ various techniques to enhance the current handling capabilities of batteries and improve charging times. For instance, expensive batteries may have a higher C-rate and incorporate new materials to withstand higher currents and temperatures. Batteries with multiple anode and cathode tabs can reduce internal resistance and increase current flow. Dual-cell batteries split the current between two parallel batteries, creating the illusion of faster charging.
Optimizing battery charge times now involves monitoring voltage and current, as well as employing optimized algorithms. This data, along with temperature information, can be utilized by intelligent chargers to optimize power delivery to devices like smartphones. So, in simple terms we can say that, To enable faster charging, manufacturers typically either increase the amperage or vary the voltage to enhance the potential energy delivered to the device. In most fast charging standards, voltage variation is the preferred approach rather than boosting the amperage.
Standard USB 3.0 ports typically provide an output of 5V/1A, suitable for smaller devices such as wearables. Most phones and other devices can handle an output of 5V/2.4A. For fast charging, manufacturers increase the voltage from 5V to 9V, 12V, or higher, or they raise the amperage to 3A or above. USB-C currently supports up to 240W and 48V power, allowing for faster charging speeds and thus promoting charging efficiency for high-end electronic devices.
Fast Charging Standard Table.
The demand for fast charging has increased exponentially in recent years. People no longer have the patience to wait for hours for their devices to charge fully. They want to get back up and running in a matter of minutes. Manufacturers have recognized this need and have come up with various fast charging standards to cater to the ever-growing market. There are multiple types of fast charging standards in the market, Read about the common USB fast charging protocol types in the mobile phone market. Common fast charging specifications include:
| Fast Charging Standard | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fast Charging Standard | Description | Compatible Devices |
| Qualcomm Quick Charge | Accelerates charging on compatible devices, delivering high wattages for faster power delivery. | Devices supporting Quick Charge |
| USB Power Delivery (PD) | A universal standard facilitating rapid charging for a range of devices using USB-C connectivity. | Various smartphones, laptops |
| Adaptive Fast Charging | Samsung’s technology adjusts voltage levels to enable quicker charging compared to standard. | Samsung smartphones |
| VOOC/SuperVOOC | Utilizes higher current at lower voltages for swift and safe charging without excessive heat. | OPPO smartphones |
| Dash Charge/Warp Charge | OnePlus’s proprietary technology optimizes voltage and current to maintain consistent speeds. | OnePlus smartphones |
| Huawei SuperCharge | Balances voltage and current for faster charging without compromising battery longevity. | Huawei smartphones |
Which Charging Standards Support Fast Charge?
USB Power Delivery (USB-PD) and Qualcomm Quick Charge are widely recognized as the original and most popular fast charging standards. Other fast charging technologies, such as TurboPower, Adaptive Fast Charging, and SuperCharge, are often derived from or built upon Qualcomm Quick Charge, albeit rebranded for marketing purposes.
When it comes to charging our devices, speed is of the essence. Whether it’s our smartphones, laptops, or electric vehicles, fast charging has become a necessity in today’s fast-paced world. But which charging standards support fast charging? In this section, we will explore the various charging standards that enable fast charging and discuss their features and compatibility.
USB Power Delivery:
USB Power Delivery (USB PD) is an official fast charging specification introduced by the USB-IF in 2012. It has gained widespread adoption in the smartphone industry, particularly since 2020. While many phones still support proprietary fast charging standards, USB PD has become the preferred choice for devices with USB-C ports.
Similar to other fast charging standards, USB PD utilizes a data protocol that facilitates communication between the charger and the device. This negotiation establishes the maximum power delivery capability for both the charger and the handset. USB PD supports a wide range of power levels, ranging from 0.5W to 100W.
USB PD PPS (Programmable Power Supply) has become increasingly prevalent in recent times. This optional feature of the USB PD specification offers more flexible voltage control in 20mV increments, resulting in more optimized fast charging capabilities. Examples of smartphones that utilize USB PD PPS include the Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra and the Pixel 7 series.
Qualcomm Quick Charge:
Qualcomm’s Quick Charge technology, while not as dominant in the smartphone charging landscape as it once was, remains relevant with its fifth-generation iteration. Despite the rise of proprietary and USB PD standards, Quick Charge is still present in a range of smartphones.
The latest version, Quick Charge 5, maintains backward compatibility with previous Quick Charge versions and also supports the USB PD specification. It can deliver up to 100W of power, catering to the needs of power-hungry devices. This represents a significant increase compared to earlier versions, which typically provided 18W or 27W of power to compatible devices.
Quick Charge 5 features incremental operating voltages of up to 20V and current ranging from 3A to 5A, closely resembling the fast charging capabilities of USB PD PPS. Qualcomm enhances its standard with charger identification capabilities, as well as protocols for voltage, current, and thermal protection. According to Qualcomm, Quick Charge 5 is designed to offer even greater safety than the USB PD standard.
Apple Fast Charging:
Since the iPhone 8, all Apple phones have supported fast charging. However, if you continue to use an older iPhone power adapter, you will only receive 5W of power and won’t fully utilize the fast charging capabilities of newer devices.
Apple utilizes USB Power Delivery for fast charging and claims that you can achieve a 50% increase in battery life within just 30 minutes. To achieve these speeds, you need to use an adapter with a minimum power output of 18W and a USB-C-to-Lightning cable. While using a more powerful adapter won’t harm your phone, it is unlikely to result in faster charging.
MediaTek Pump Express:
Certain smartphones powered by MediaTek chips utilize MediaTek’s Pump Express standard, which varies across different devices.
Pump Express 2.0+ is primarily designed for MediaTek’s low-end chipsets and is compatible with micro USB and USB-C charging ports. It supports charging speeds of up to 15W by utilizing variable voltage ranging from 5V to 20V, along with 3A or 4.5A of current.
Pump Express 3.0 and Pump Express 4.0 are similar in terms of current, both supporting 5A. They also incorporate USB Power Delivery 3.0. The difference lies in Pump Express 4.0’s additional support for proprietary wireless charging technology, as well as Qi wireless charging at 5W.
MediaTek claims that Pump Express 2.0+ can charge a depleted battery to 70% within 30 minutes, while Pump Express 3.0 and 4.0 can achieve even faster charging times, cutting that time in half. However, in our testing, we observed an average of around 55% charge in 15 minutes for Pump Express 3.0, which is still quite impressive.
Motorola Rapid Charging and TurboPower:
Motorola employs two proprietary fast charging standards: Rapid Charging and TurboPower. Older Motorola phones (up to 2021) generally utilize Rapid Charging, which delivers 10W charging through micro USB or USB-C. It offers a slight improvement over basic 5W charging but does not provide exceptionally fast charging times.
Mid-range and flagship Motorola phones, on the other hand, utilize TurboPower technology. TurboPower standards vary, with some reaching up to 68W. However, most Motorola phones do not support such high speeds, and the 68W charging is specifically recommended for the Motorola Edge+. To simplify matters, all Motorola smartphones with TurboPower also support Qualcomm Quick Charge 3.0.
| Voltage | Current | Max power | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TurboPower 15 | 9V/12V | 1.2A/1.67A | 15W |
| TurboPower 25 | 5V/9V/12V | 2.15A/2.85A | 25W |
| TurboPower 30 | 5V | 5.7A | 28.5W |
OnePlus Dash Charge and Warp Charge:
OnePlus adopts Warp Charge technology, which is licensed from and functions similarly to Oppo’s Vooc. In the OnePlus 10 Pro with Warp Charge, the power output can reach up to 65W, enabling a full charge in approximately 40 minutes. Wired charging is achieved through a 5V/6A adapter and a proprietary USB-C cable. Wireless charging at 30W presents challenges due to heat generation, so OnePlus employs a lower voltage of 20V at 1.5A to minimize heat.
Older OnePlus smartphones utilize Dash Charge, which supports charging speeds of up to 20W. However, OnePlus 8 and newer devices come with Warp Charge and its significantly improved charging speeds.
| Voltage | Current | Max power | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dash Charge | 5V | 4A | 20W |
| Warp Charge | 5V | 6A | 30W |
| Warp Charge 30T | 5V | 6A | 30W |
| Warp Charge 65T | 5V | 6A | 65W |
| Oppo VOOC | 5V | 5A | 25W |
| Oppo Super VOOC | 10V | 5A | 50W |
Oppo SuperVooc Flash Charge:
Oppo’s proprietary fast charging standard is called Vooc. Oppo has been at the forefront of fast charging technology and currently holds the record for the fastest charging speed with its 240W SuperVooc technology, capable of fully charging a 4,500mAh battery in just nine minutes. Additionally, Oppo incorporates gallium nitride (GaN) batteries in its phones for enhanced performance and reliability.
Oppo’s SuperVooc technology comes in various versions. SuperVooc Flash Charge offers 65W charging using 10V and 6.5A. SuperVooc 2.0 achieves a maximum charge of 65W by combining 10V of electrical force with 5A of power, although its charging times are slightly slower. Vooc 4.0, introduced in 2020, offers a maximum charging speed of 30W at 5V/6A.
To achieve these high charging speeds, Oppo phones require a special USB-C cable and adapter.
While each fast charging standard comes with its own benefits, it’s important to note that compatibility can vary across different devices and chargers. Some devices may only support specific charging standards, while others may be compatible with multiple standards.
To ensure fast charging compatibility, it is important to use chargers and cables that are certified for the specific charging standard supported by your device. Mixing and matching different standards could result in slower charging speeds or even damage to the device or charger.
The smartphone market in 2023 has witnessed a consolidation of fast charging standards, both wired and wireless. The PD&QC protocol has become the dominant standard for Android and Apple fast chargers, marking a significant shift from the proliferation of various charging protocols in previous years.
Especially the latest PD3.1 is also very popular in the laptop market. The high power transmission of up to 240W allows users to quickly charge multiple devices using a single multi-port wall adapter.
The newly emerging wireless charging industry in recent years has followed a similar trajectory, with various brands adopting the Qi standard as an industry norm. Although Qi standard wireless charging is not as fast as wired charging, its convenience and sense of technology are still loved by the public.
Fast charging has revolutionized the way we power our devices, offering rapid and efficient charging solutions. By harnessing advanced technologies such as USB Power Delivery and Quick Charge, fast chargers deliver higher power outputs, reducing charging times significantly. As we continue to rely on our devices for various tasks, a reliable fast charger becomes an essential accessory.
APPHONE stands out as a trusted manufacturer of fast charging solutions. With a focus on innovation, efficiency, and safety, APPHONE offers a diverse range of fast chargers tailored to meet your specific needs. Our products are backed by authoritative certifications, ensuring high-quality and reliable performance. Whether you’re in need of a USB C PD wall charger, a QC 3.0 USB A car charger, or a multi-port charger adapter, APPHONE has you covered.
Is fast charging safe?
Fast charging can have potential risks if not used with certified accessories. It is important to ensure that your fast charging accessories, such as chargers and cables, are certified and compatible with your smartphone. Certified accessories meet safety and performance standards, reducing the risk of overheating or shorting that can damage your device and charger.
Reputable manufacturers produce chargers that may get warm during use but are safe when certified and compatible. These certified chargers have E Marker controller chips that regulate electricity flow to the battery, preventing dangerous spikes in current. Temperature and voltage controls ensure the charger operates within safe limits.
What is the fast charging method?
Fast charging methods typically involve delivering a higher voltage and amperage to the device during the charging process. This can be achieved through various technologies such as USB Power Delivery (USB-PD) or Qualcomm Quick Charge. These methods optimize the charging circuitry and power delivery capabilities to enable faster charging speeds.
What is the theory of fast charging?
The theory behind fast charging is to deliver a higher electrical power (amperage) to the device being charged compared to standard charging. By increasing the electrical transfer rate, fast charging reduces the charging time significantly, allowing devices to charge at a faster pace.
What are the rules for fast charging?
The rules for fast charging include using a compatible charger and cables, avoiding extreme temperatures, charging with the screen off, and preventing overcharging.
How to make your phone charge faster?
To make your phone charge faster:
- Use a fast charger.
- Enable Airplane Mode.
- Close background apps.
- Remove the phone case.
- Use a high-quality USB cable.
- Avoid using the phone while charging.
- Keep the phone cool.
- Optimize battery usage.
Does fast charge affect battery life?
Fast charging can have a slight impact on battery life due to increased heat generation, but modern smartphones are designed to handle it. Using certified accessories, avoiding extreme temperatures, and not consistently charging to full capacity can help mitigate any potential effects on battery health.
Why doesn't fast charging work?
The problem of your phone not charging fast can be as a result of your cable being faulty. When a cable is too old it can slow down the rate at which your phone should typically charge. Change the cable if this is the suspected case. Also, your charging port may be the issue for your phone not charging fast.
What is Adaptive Quick Charging?
Adaptive Fast Charging, TurboPower, and SuperCharge are branding terms used by manufacturers to describe their fast charging technologies.
These technologies are based on established standards like Quick Charge or USB Power Delivery. For instance, Adaptive Fast Charging by Samsung is based on Quick Charge, while TurboPower by Motorola and SuperCharge by Huawei/Honor are based on USB PD. Specifically designed for battery health and essentially ensuring that your battery capacity remains close to 100% for as long as possible.
Ready To Fast Charge?
Welcome to APPHONE, your trusted partner for innovative Fast Charger solutions. We offer diverse, high-efficiency, and safe customized charging products. With authoritative certifications like UL, CE, FCC, and RoHS, we ensure high-quality and high-safety standards.
Our range includes USB C PD wall chargers (up to 100W), QC 3.0 USB A car chargers (up to 45W), and multi-port 65Gan charger adapters for lightweight and efficient charging.
Whether at home, the office, or in your car, our Fast Chargers provide fast and stable charging for your devices. Contact us today to explore our multi-interface Fast Charger products and customization options for a future-grade smart charging experience.
Share This Artcle:

Fast delivery
Fastest delivery within 22 days

Quick proofing
Fastest 3-day proofing cycle

After-sale protection
24-month long warranty

1V1Customer Service
Professional customer service follow-up